Metal-ion binding to high-energy N12C4
- PMID: 19527014
- PMCID: PMC2733847
- DOI: 10.1021/jp900561z
Metal-ion binding to high-energy N12C4
Abstract
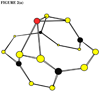
Carbon-nitrogen compounds are of interest for their potential as high-energy materials. One major issue in determining the structures of high-energy materials is molecular stability; a more stable energetic compound is more likely to be useful in a wider variety of applications. In this study, binding energies are calculated for a high-energy N(12)C(4) structure with a series of metal ions to determine preferred binding sites. A metal ion bound to the molecule at a preferred site may stabilize the molecule and render it more potentially useful. The results are calculated on using the PBE1PBE density functional method with the cc-pVDZ basis set of Dunning. Trends in binding energies are calculated and discussed with respect to both the identity of the ion and the various binding sites on the N(12)C(4) molecule.
Figures



References
-
- Fau S, Bartlett RJ. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2001;105:4096.
-
- Tian A, Ding F, Zhang L, Xie Y, Schaefer HF., III J. Phys. Chem. A. 1997;101:1946.
-
- Chung G, Schmidt MW, Gordon MS. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2000;104:5647.
-
- Strout DL. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2002;106:816.
-
- Thompson MD, Bledson TM, Strout DL. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2002;106:6880.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

