Location, structure, and dynamics of the synthetic cannabinoid ligand CP-55,940 in lipid bilayers
- PMID: 19527650
- PMCID: PMC2712040
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.03.033
Location, structure, and dynamics of the synthetic cannabinoid ligand CP-55,940 in lipid bilayers
Abstract
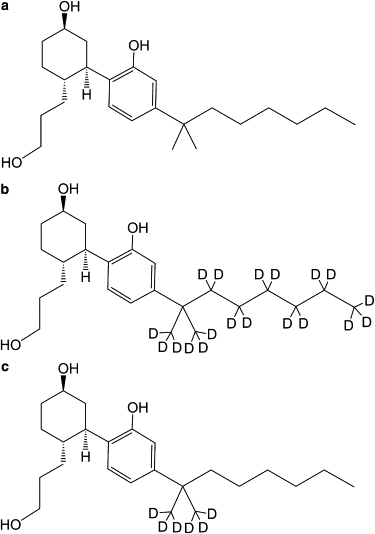
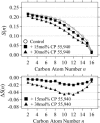
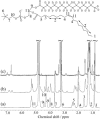
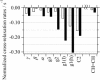
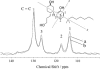
The widely used hydrophobic cannabinoid ligand CP-55,940 partitions with high efficiency into biomembranes. We studied the location, orientation, and dynamics of CP-55,940 in POPC bilayers by solid-state NMR. Chemical-shift perturbation of POPC protons from the aromatic ring-current effect, as well as 1H NMR cross-relaxation rates, locate the hydroxyphenyl ring of the ligand near the lipid glycerol, carbonyls, and upper acyl-chain methylenes. Order parameters of the hydroxyphenyl ring determined by the 1H-13C DIPSHIFT experiment indicate that the bond between the hydroxyphenyl and hydroxycyclohexyl rings is oriented perpendicular to the bilayer normal. 2H NMR order parameters of the nonyl tail are very low, indicating that the hydrophobic chain maintains a high level of conformational flexibility in the membrane. Lateral diffusion rates of CP-55,940 and POPC were measured by 1H magic-angle spinning NMR with pulsed magnetic field gradients. The rate of CP-55,940 diffusion is comparable to the rate of lipid diffusion. The magnitude of cross-relaxation and diffusion rates suggests that associations between CP-55,940 and lipids are with lifetimes of a fraction of a microsecond. With its flexible hydrophobic tail, CP-55,940 may efficiently approach the binding site of the cannabinoid receptor from the lipid-water interface by lateral diffusion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The conformational properties of the highly selective cannabinoid receptor ligand CP-55,940.J Biol Chem. 1996 May 3;271(18):10640-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.18.10640. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8631869
-
Structural divergence among cannabinoids influences membrane dynamics: a 2H solid-state NMR analysis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Sep;1768(9):2049-59. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.04.023. Epub 2007 May 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17555706
-
The interaction of cannabinoid receptor agonists, CP55940 and WIN55212-2 with membranes using solid state 2H NMR.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Sep;1808(9):2095-101. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.11.026. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21129361 Free PMC article.
-
How lipophilic cannabinergic ligands reach their receptor sites.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005 Sep;77(1-4):210-8. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2004.01.010. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005. PMID: 16099405 Review.
-
Lipid lateral diffusion and membrane heterogeneity.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1788(1):234-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.08.016. Epub 2008 Sep 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18805393 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of essential cannabinoid-binding domains: structural insights into early dynamic events in receptor activation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 23;286(38):33422-35. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.261651. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21795705 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Dynamics Methodologies for Probing Cannabinoid Ligand/Receptor Interaction.Methods Enzymol. 2017;593:449-490. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2017.05.004. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Methods Enzymol. 2017. PMID: 28750815 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilization of functional recombinant cannabinoid receptor CB(2) in detergent micelles and lipid bilayers.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46290. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046290. Epub 2012 Oct 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23056277 Free PMC article.
-
Lipophilicity Modulations by Fluorination Correlate with Membrane Partitioning.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023 May 15;62(21):e202301077. doi: 10.1002/anie.202301077. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023. PMID: 36932824 Free PMC article.
-
Special issue for Klaus Gawrisch.Biophys J. 2023 Mar 21;122(6):E1-E8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.02.022. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36921597 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Matsuda L.A., Lolait S.J., Brownstein M.J., Young A.C., Bonner T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional expression of the cloned cDNA. Nature. 1990;346:561–564. - PubMed
-
- Munro S., Thomas K.L., Abu-Shaar M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature. 1993;365:61–65. - PubMed
-
- Sugiura T., Kondo S., Sukagawa A., Nakane S., Shinoda A. 2-Arachidonoylgylcerol: a possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995;215:89–97. - PubMed
-
- Mechoulam R., Ben-Shabat S., Hanus L., Ligumsky M., Kaminski N.E. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995;50:83–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

