Structured event complexes in the medial prefrontal cortex support counterfactual representations for future planning
- PMID: 19528010
- PMCID: PMC2666713
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0315
Structured event complexes in the medial prefrontal cortex support counterfactual representations for future planning
Abstract
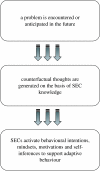
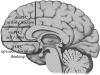
We propose that counterfactual representations for reasoning about the past or predicting the future depend on structured event complexes (SECs) in the human prefrontal cortex (PFC; 'What would happen if X were performed in the past or enacted in the future?'). We identify three major categories of counterfactual thought (concerning action versus inaction, the self versus other and upward versus downward thinking) and propose that each form of inference recruits SEC representations in distinct regions of the medial PFC. We develop a process model of the regulatory functions these representations serve and draw conclusions about the importance of SECs for explaining the past and predicting the future.
Figures

References
-
- Barbey, A. K. & Barsalou, L. W. 2009 Reasoning and problem solving: models. In New encyclopedia of neuroscience, vol. 3 (eds L. Squire, T. Albright, F. Bloom, F. Gage & N. Spitzer), pp. 35–43. Oxford, UK: Elsevier.
-
- Barbey A.K., Sloman S.A. Base-rate respect: from ecological rationality to dual processes. Behav. Brain Sci. 2007;30:241–297. doi:10.1017/S0140525x07001653 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barbey, A. K. & Wolff, P. 2006 Causal reasoning from forces. In Proc. 28th Annual Conf. Cognitive Science Society Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
-
- Barbey, A. K. & Wolff, P. 2007 Learning causal structure from reasoning. In Proc. 29th Annual Conf. Cognitive Science Society Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum Press.
-
- Barbey, A. K. & Wolff, P. Submitted. Composing causal relations in force dynamics.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
