MaXIC-Q Web: a fully automated web service using statistical and computational methods for protein quantitation based on stable isotope labeling and LC-MS
- PMID: 19528069
- PMCID: PMC2703943
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp476
MaXIC-Q Web: a fully automated web service using statistical and computational methods for protein quantitation based on stable isotope labeling and LC-MS
Abstract
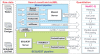
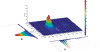
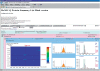
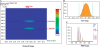
Isotope labeling combined with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) provides a robust platform for analyzing differential protein expression in proteomics research. We present a web service, called MaXIC-Q Web (http://ms.iis.sinica.edu.tw/MaXIC-Q_Web/), for quantitation analysis of large-scale datasets generated from proteomics experiments using various stable isotope-labeling techniques, e.g. SILAC, ICAT and user-developed labeling methods. It accepts spectral files in the standard mzXML format and search results from SEQUEST, Mascot and ProteinProphet as input. Furthermore, MaXIC-Q Web uses statistical and computational methods to construct two kinds of elution profiles for each ion, namely, PIMS (projected ion mass spectrum) and XIC (extracted ion chromatogram) from MS data. Toward accurate quantitation, a stringent validation procedure is performed on PIMSs to filter out peptide ions interfered with co-eluting peptides or noise. The areas of XICs determine ion abundances, which are used to calculate peptide and protein ratios. Since MaXIC-Q Web adopts stringent validation on spectral data, it achieves high accuracy so that manual validation effort can be substantially reduced. Furthermore, it provides various visualization diagrams and comprehensive quantitation reports so that users can conveniently inspect quantitation results. In summary, MaXIC-Q Web is a user-friendly, interactive, robust, generic web service for quantitation based on ICAT and SILAC labeling techniques.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Automated generic analysis tools for protein quantitation using stable isotope labeling.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;604:257-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-444-9_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20013376
-
The Multi-Q web server for multiplexed protein quantitation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W707-12. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm345. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17553828 Free PMC article.
-
IDEAL-Q, an automated tool for label-free quantitation analysis using an efficient peptide alignment approach and spectral data validation.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Jan;9(1):131-44. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900177-MCP200. Epub 2009 Sep 13. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 19752006 Free PMC article.
-
Open source libraries and frameworks for mass spectrometry based proteomics: a developer's perspective.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan;1844(1 Pt A):63-76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.02.032. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23467006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods and Algorithms for Quantitative Proteomics by Mass Spectrometry.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2051:161-197. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9744-2_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31552629 Review.
Cited by
-
A critical appraisal of techniques, software packages, and standards for quantitative proteomic analysis.OMICS. 2012 Sep;16(9):431-42. doi: 10.1089/omi.2012.0022. Epub 2012 Jul 17. OMICS. 2012. PMID: 22804616 Free PMC article.
-
Target identification and mechanism of action in chemical biology and drug discovery.Nat Chem Biol. 2013 Apr;9(4):232-40. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1199. Nat Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 23508189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SILACtor: software to enable dynamic SILAC studies.Anal Chem. 2011 Nov 15;83(22):8403-10. doi: 10.1021/ac2017053. Epub 2011 Oct 27. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21954881 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tao WA, Aebersold R. Advances in quantitative proteomics via stable isotope tagging and mass spectrometry. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003;14:110–118. - PubMed
-
- Gygi SP, Rist B, Gerber SA, Turecek F, Gelb MH, Aebersold R. Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999;17:994–999. - PubMed
-
- Yao X, Freas A, Ramirez J, Demirev PA, Fenselau C. Proteolytic 18O labeling for comparative proteomics: model studies with two serotypes of adenovirus. Anal. Chem. 2001;73:2836–2842. - PubMed
-
- Ong SE, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A, Mann M. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2002;1:376–386. - PubMed
-
- Ong SE, Mann M. A practical recipe for stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:2650–2660. - PubMed

