Translation of intronless RNAs is strongly stimulated by the Epstein-Barr virus mRNA export factor EB2
- PMID: 19528074
- PMCID: PMC2731895
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp497
Translation of intronless RNAs is strongly stimulated by the Epstein-Barr virus mRNA export factor EB2
Abstract
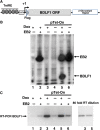
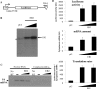
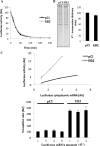
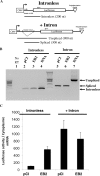
The Epstein-Barr virus protein (EB2) allows the nuclear export of a particular subset of early and late viral RNAs derived from intronless genes. EB2 is conserved among most herpesvirus members and its presence is essential for the production of infectious particles. Here we show that, besides its role as a nuclear export factor, EB2 strongly stimulates translation of unspliced mRNAs without affecting overall cellular translation. Interestingly, this effect can be reversed by the addition of an intron within the gene. The spliced mRNA is then efficiently exported and translated even in the absence of EB2. Moreover, we show that EB2 associates with translating ribosomes and increases the proportion of its target RNA in the polyribosomal fraction. Finally, testing of EB2 homolog proteins derived from EBV-related herpesviruses, shows that, even if they play similar roles within the replication cycle of their respective virus, their mechanisms of action are different.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Protein EB2 Stimulates Translation Initiation of mRNAs through Direct Interactions with both Poly(A)-Binding Protein and Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4G.J Virol. 2018 Jan 17;92(3):e01917-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01917-17. Print 2018 Feb 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29142127 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus mRNA export factor EB2 is essential for intranuclear capsid assembly and production of gp350.J Virol. 2005 Nov;79(22):14102-11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.22.14102-14111.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254345 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) protein EB is an mRNA export factor essential for virus production.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:3798-813. doi: 10.2741/2969. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508475
-
The human cytomegalovirus regulatory protein UL69 and its effect on mRNA export.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2939-49. doi: 10.2741/2899. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981767 Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 and ZEBRA: targets for therapeutic strategies against EBV-carrying cancers.J Pathol. 2015 Jan;235(2):334-41. doi: 10.1002/path.4431. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25186125 Review.
Cited by
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 protein interacts with PYM to enhance translation of viral intronless mRNAs.EMBO J. 2010 Jun 2;29(11):1851-64. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.77. Epub 2010 Apr 30. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20436455 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced Nodules on Viral Replication Compartments Contain RNA Processing Proteins and a Viral Long Noncoding RNA.J Virol. 2018 Sep 26;92(20):e01254-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01254-18. Print 2018 Oct 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30068640 Free PMC article.
-
Different effects of the TAR structure on HIV-1 and HIV-2 genomic RNA translation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(6):2653-67. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1093. Epub 2011 Nov 24. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22121214 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus Protein EB2 Stimulates Translation Initiation of mRNAs through Direct Interactions with both Poly(A)-Binding Protein and Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 4G.J Virol. 2018 Jan 17;92(3):e01917-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01917-17. Print 2018 Feb 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29142127 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of a microRNA response in trans reveals a new role for poly(A) in translational repression.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jul;39(12):5215-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr086. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21385827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moore MJ, Proudfoot NJ. Pre-mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell. 2009;136:688–700. - PubMed
-
- Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N. eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999;68:913–963. - PubMed
-
- Prevot D, Darlix JL, Ohlmann T. Conducting the initiation of protein synthesis: the role of eIF4G. Biol. Cell. 2003;95:141–156. - PubMed
-
- Le Hir H, Nott A, Moore MJ. How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2003;28:215–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

