Trajectory of declines in physical activity in community-dwelling older women: social cognitive influences
- PMID: 19528360
- PMCID: PMC2728090
- DOI: 10.1093/geronb/gbp049
Trajectory of declines in physical activity in community-dwelling older women: social cognitive influences
Abstract
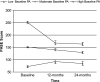
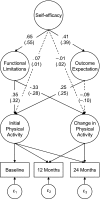
Studies examining physical activity behavior suggest that activity levels decline with age. Such declines are particularly problematic among older adults in light of the research suggesting a protective effect of physical activity on numerous physical health outcomes associated with independent living. Despite a growing recognition of the importance of a physically active lifestyle, little is known about the role of demographic and psychosocial variables on this trajectory of change. In this study, the roles played by outcome expectations, self-efficacy, and functional limitations on changes in physical activity levels over a 2-year period in older women were assessed using latent growth curve modeling. Data were obtained from 249 community-dwelling older women (M age = 68.12, n = 81 Black, and n = 168 White). Demographic, health status, and psychosocial data were collected via self-report upon entry into the study. Self-reported physical activity was assessed at baseline and again at 12 and 24 months. As expected, physical activity declined over the 2-year period. Self-efficacy demonstrated an indirect association with the trajectory of decline in physical activity through functional limitations. Importantly, the pattern of relationships appears independent of demographic factors and chronic health conditions.
Figures
References
-
- Bandura A. Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1986.
-
- Bandura A. Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: W.H. Freeman; 1997.
-
- Bandura A. Health promotion by social cognitive means. Health Education & Behavior. 2004;31:143–164. - PubMed
-
- Bentler PM. Comparative fit indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin. 1990;107:238–246. - PubMed
-
- Browne MW, Cudeck R. Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In: Bollen KA, Long JS, editors. Testing structural equation models. Newbury Park, CA: Sage; 1993. pp. 136–162.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

