Review of disrupted sleep patterns in Smith-Magenis syndrome and normal melatonin secretion in a patient with an atypical interstitial 17p11.2 deletion
- PMID: 19530184
- PMCID: PMC2760428
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32846
Review of disrupted sleep patterns in Smith-Magenis syndrome and normal melatonin secretion in a patient with an atypical interstitial 17p11.2 deletion
Abstract
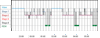
Smith-Magenis syndrome (SMS) is a disorder characterized by multiple congenital anomalies and behavior problems, including abnormal sleep patterns. It is most commonly due to a 3.5 Mb interstitial deletion of chromosome 17 band p11.2. Secretion of melatonin, a hormone produced by the pineal gland, is the body's signal for nighttime darkness. Published reports of 24-hr melatonin secretion patterns in two independent SMS cohorts (US and France) document an inverted endogenous melatonin pattern in virtually all cases (96%), suggesting that this finding is pathognomic for the syndrome. We report on a woman with SMS due to an atypical large proximal deletion ( approximately 6Mb; cen<->TNFRSFproteinB) of chromosome band (17)(p11.2p11.2) who presents with typical sleep disturbances but a normal pattern of melatonin secretion. We further describe a melatonin light suppression test in this patient. This is the second reported patient with a normal endogenous melatonin rhythm in SMS associated with an atypical large deletion. These two patients are significant because they suggest that the sleep disturbances in SMS cannot be solely attributed to the abnormal diurnal melatonin secretion versus the normal nocturnal pattern.
Figures




References
-
- Bi W, Saifi GM, Girirajan S, Shi X, Szomju B, Firth H, Magenis RE, Potocki L, Elsea SH, Lupski JR. RAI1 point mutations, CAG repeat variation, and SNP analysis in non-deletion Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140(22):2454–2463. - PubMed
-
- Cornelissen G, Halberg F, Tarquini R, Perfetto F, Salti R, Laffi G, Otsuka K. Point and interval estimations of circadian melatonin ecphasia in Smith-Magenis syndrome. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57 Suppl 1:31s–34s. - PubMed
-
- Czeisler CA, Shanahan TL, Klerman EB, Martens H, Brotman DJ, Emens JS, Klein T, Rizzo JF. Suppression of Melatonin Secretion in Some Blind Patients by Exposure to Bright Light. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(1):6–11. - PubMed
-
- Danel T, Touitou Y. Alcohol Consumption Does Not Affect Melatonin Circadian Synchronization in Healthy Men. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006;41(4):386–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

