Plasmid-encoded interleukin-15 receptor alpha enhances specific immune responses induced by a DNA vaccine in vivo
- PMID: 19530914
- PMCID: PMC2829284
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2009.025
Plasmid-encoded interleukin-15 receptor alpha enhances specific immune responses induced by a DNA vaccine in vivo
Abstract
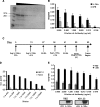
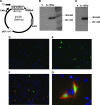
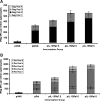
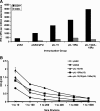
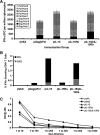
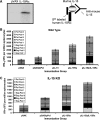
Plasmid-encoded DNA vaccines appear to be a safe and effective method for delivering antigen; however, the immunogenicity of such vaccines is often suboptimal. Cytokine adjuvants including interleukin (IL)-12, RANTES, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IL-15, and others have been used to augment the immune response against DNA vaccines. In particular, IL-15 binds to a unique high-affinity receptor, IL-15R alpha; is trans-presented to CD8(+) T cells expressing the common betagamma chain; and has been shown to play a role in the generation, maintenance, and proliferation of antigen-specific CD8(+) T cells. In this study, we took the unique approach of using both a cytokine and its receptor as an adjuvant in an HIV-1 vaccine strategy. To study IL-15R alpha expression, a unique monoclonal antibody (KK1.23) was generated to confirm receptor expression in vitro. Coimmunization of IL-15 and IL-15R alpha plasmids with HIV-1 antigenic plasmids in mice enhanced the antigen-specific immune response 2-fold over IL-15 immunoadjuvant alone. Furthermore, plasmid-encoded IL-15R alpha augments immune responses in the absence of IL-15, suggesting its role as a novel adjuvant. Moreover, pIL-15R alpha enhanced the cellular, but not the humoral, immune response as measured by antigen-specific IgG antibody. This is the first report describing that IL-15R alpha itself can act as an adjuvant by enhancing an antigen-specific T cell response. Uniquely, pIL-15 and pIL-15R alpha adjuvants combined, but not the receptor alpha chain alone, may be useful as a strategy for generating and maintaining memory CD8(+) T cells in a DNA vaccine.
Figures

Comment in
-
Gene-based adjuvants: a new meaning.Hum Gene Ther. 2009 Oct;20(10):1101-2. doi: 10.1089/hum.2009.910. Hum Gene Ther. 2009. PMID: 19848597 No abstract available.
References
-
- Amara R.R. Villinger F. Altman J.D. Lydy S.L. O'Neil S.P. Staprans S.I. Montefiori D.C. Xu Y. Herndon J.G. Wyatt L.S. Candido M.A. Kozyr N.L. Earl P.L. Smith J.M. Ma H.L. Grimm B.D. Hulsey M.L. Miller J. McClure H.M. McNicholl J.M. Moss B. Robinson H.L. Control of a mucosal challenge and prevention of AIDS by a multiprotein DNA/MVA vaccine. Science. 2001;292:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D.M. Johnson L. Glaccum M.B. Copeland N.G. Gilbert D.J. Jenkins N.A. Valentine V. Kirstein M.N. Shapiro D.N. Morris S.W. Grabstein K. Cosman D. Chromosomal assignment and genomic structure of Il15. Genomics. 1995a;25:701–706. - PubMed
-
- Anderson D.M. Kumaki S. Ahdieh M. Bertles J. Tometsko M. Loomis A. Giri J. Copeland N.G. Gilbert D.J. Jenkins N.A. Valentine V. Shapiro D.N. Morris S.W. Park L.S. Cosman D. Functional characterization of the human interleukin-15 receptor α chain and close linkage of IL15RA and IL2RA genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995b;270:29862–29869. - PubMed
-
- Bamford R.N. Defilippis A.P. Azimi N. Kurys G. Waldmann T.A. The 5′ untranslated region, signal peptide, and the coding sequence of the carboxyl terminus of IL-15 participate in its multifaceted translational control. J. Immunol. 1998;160:4418–4426. - PubMed
-
- Barouch D.H. Santra S. Schmitz J.E. Kuroda M.J. Fu T.M. Wagner W. Bilska M. Craiu A. Zheng X.X. Krivulka G.R. Beaudry K. Lifton M.A. Nickerson C.E. Trigona W.L. Punt K. Freed D.C. Guan L. Dubey S. Casimiro D. Simon A. Davies M.E. Chastain M. Strom T.B. Gelman R.S. Montefiori D.C. Lewis M.G. Emini E.A. Shiver J.W. Letvin N.L. Control of viremia and prevention of clinical AIDS in rhesus monkeys by cytokine-augmented DNA vaccination. Science. 2000;290:486–492. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

