Epidemiology of HIV-associated tuberculosis
- PMID: 19532072
- PMCID: PMC4233405
- DOI: 10.1097/COH.0b013e32832c7d61
Epidemiology of HIV-associated tuberculosis
Abstract
Purpose of review: We review literature concerning the epidemiology of HIV-associated tuberculosis (HIV-TB), focusing on articles published between 2007 and 2008.
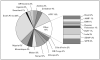
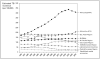
Recent findings: An estimated 1.37 million new cases of HIV-TB occurred in 2007, representing 15% of the total global burden of TB. In addition, an estimated 456 000 HIV-TB deaths accounted for 23% of global HIV/AIDS mortality. Sub-Saharan Africa is the worst affected region with 79% of the disease burden. The epicentre of the coepidemic lies in the south of the continent, with South Africa alone accounting for over one quarter of all cases. A critical overlap between HIV and the global multidrug-resistant TB epidemics is emerging. Although it is as yet unclear whether HIV is driving a disproportionate increase in multidrug-resistant TB cases at a population level, HIV has nevertheless been a potent risk factor for institutional outbreaks, especially in South Africa and eastern Europe. Increasing data have highlighted the risk of TB among HIV-infected healthcare workers in resource-limited settings. However, many studies also show the major benefits to be derived from antiretroviral therapy in high-income and low-income countries.
Summary: HIV-TB remains a major challenge to global health that requires substantial increases in resource allocation and concerted international action.
Figures

References
-
- Rieder HL, Cauthen GM, Comstock GW, Snider DE., Jr Epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States. Epidemiol Rev. 1989;11:79–98. - PubMed
-
- Corbett EL, Watt CJ, Walker N, Maher D, Williams BG, Raviglione MC, et al. The growing burden of tuberculosis: global trends and interactions with the HIV epidemic. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:1009–1021. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis control, 2009. Epidemiology, strategy, financing. World Health Organization; Geneva: WHO/HTM/TB/2009.411. [** A comprehensive overview of the burden of TB at global, regional and national levels with data available up to 2007. In this report, increasing availability of data have permitted the estimates of the burden of HIV-TB to be revised. These find almost double the number of cases occur each year than was previously estimated.]
-
- World Health Organization . Global Tuberculosis Control. Surveillance, planning and financing. World Health Organization; Geneva: 2008. WHO/HTM/TB/2008.393. [* A comprehensive annual overview of the burden of tuberculosis at the global, regional and national levels using data available up to 2006.]
-
- Lazarus JV, Olsen M, Ditiu L, Matic S. Tuberculosis-HIV co-infection: policy and epidemiology in 25 countries in the WHO European region. HIV Med. 2008;9:406–14. [* This paper highlights the rising trends in the burden of HIV-associated tuberculosis in several European countries,] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

