The risks and benefits of initial irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in patients with severe hypertension
- PMID: 19534037
- PMCID: PMC8672986
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2009.00109.x
The risks and benefits of initial irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy in patients with severe hypertension
Abstract
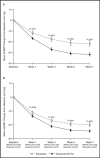
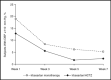
The impact of delays in blood pressure (BP) reduction is particularly relevant for patients with severe hypertension who are at risk for hypertensive emergencies. Combination therapies may hold promise as initial treatment for these patients. The safety and efficacy of initial irbesartan / hydrochlorothiazide (angiotensin receptor blocker / thiazide) treatment was compared with that of irbesartan as monotherapy in a multicenter, double-blind, parallel-group study in patients with severe hypertension. After 5 weeks, 47% of patients receiving combination therapy achieved a target diastolic BP <90 mm Hg compared with 33% with monotherapy (P=.0005). Similarly, systolic BP/ diastolic BP <140 / 90 mm Hg targets were reached by more subjects treated with combination therapy than subjects receiving monotherapy (34.6% vs 19.2%, P<.0001). Initial use of combination therapy instead of monotherapy is estimated to prevent between 250 and 4500 cardiovascular events in every 100,000 severely hypertensive patients over 5 years, without significantly increasing serious adverse event rates.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Initial combination therapy with irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension: an analysis of the relationship between baseline blood pressure and the need for combination therapy.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007 Dec;9(12 Suppl 5):15-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-6175.2007.07808.x. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2007. PMID: 18046108 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fixed combination of irbesartan and hydrochlorothiazide in the management of hypertension.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009;5(1):213-24. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s3302. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 19436667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BP goal achievement in patients with uncontrolled hypertension : results of the treat-to-target post-marketing survey with irbesartan.Clin Drug Investig. 2007;27(11):783-96. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200727110-00005. Clin Drug Investig. 2007. PMID: 17914897
-
A comparison of the efficacy and safety of irbesartan/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy with irbesartan monotherapy in the treatment of moderate or severe hypertension in diabetic and obese hypertensive patients: a post-hoc analysis review.Postgrad Med. 2011 Jul;123(4):126-34. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2011.07.2312. Postgrad Med. 2011. PMID: 21680997 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Zofenopril vs. Irbesartan in Combination with a Thiazide Diuretic in Hypertensive Patients with Multiple Risk Factors not Controlled by a Previous Monotherapy: A Review of the Double-Blind, Randomized "Z" Studies.Adv Ther. 2017 Apr;34(4):784-798. doi: 10.1007/s12325-017-0497-8. Epub 2017 Mar 4. Adv Ther. 2017. PMID: 28260186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The comparative efficacy and safety of the angiotensin receptor blockers in the management of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.Drug Saf. 2015 Jan;38(1):33-54. doi: 10.1007/s40264-014-0239-7. Drug Saf. 2015. PMID: 25416320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Effects of treatment on morbidity in hypertension. Results in patients with diastolic blood pressures averaging 115 through 129 mm Hg. JAMA. 1967;202:1028–1034. - PubMed
-
- Wolff FW, Lindeman RD. Effects of treatment in hypertension. Results of a controlled study. J Chronic Dis. 1966;19:227–240. - PubMed
-
- Preston RA, Baltodano NM, Cienki J, et al. Clinical presentation and management of patients with uncontrolled, severe hypertension: results from a public teaching hospital. J Hum Hypertens. 1999;13:249–255. - PubMed
-
- Zampaglione B, Pascale C, Marchisio M, et al. Hypertensive urgencies and emergencies. Prevalence and clinical presentation. Hypertension. 1996;27:144–147. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting. April 2007; http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/07/transcripts/2007‐4287t1‐part1.pdf. Accessed April 14, 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

