Crystal structures of human SIRT3 displaying substrate-induced conformational changes
- PMID: 19535340
- PMCID: PMC2782032
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014928
Crystal structures of human SIRT3 displaying substrate-induced conformational changes
Abstract
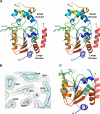
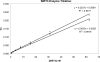
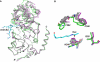
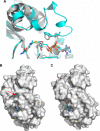
SIRT3 is a major mitochondrial NAD(+)-dependent protein deacetylase playing important roles in regulating mitochondrial metabolism and energy production and has been linked to the beneficial effects of exercise and caloric restriction. SIRT3 is emerging as a potential therapeutic target to treat metabolic and neurological diseases. We report the first sets of crystal structures of human SIRT3, an apo-structure with no substrate, a structure with a peptide containing acetyl lysine of its natural substrate acetyl-CoA synthetase 2, a reaction intermediate structure trapped by a thioacetyl peptide, and a structure with the dethioacetylated peptide bound. These structures provide insights into the conformational changes induced by the two substrates required for the reaction, the acetylated substrate peptide and NAD(+). In addition, the binding study by isothermal titration calorimetry suggests that the acetylated peptide is the first substrate to bind to SIRT3, before NAD(+). These structures and biophysical studies provide key insight into the structural and functional relationship of the SIRT3 deacetylation activity.
Figures



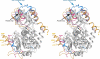
References
-
- Dutnall R. N., Pillus L. (2001) Cell 105, 161–164 - PubMed
-
- Vaquero A., Scher M., Lee D., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Reinberg D. (2004) Mol. Cell 16, 93–105 - PubMed
-
- Vaziri H., Dessain S. K., Ng Eaton E., Imai S. I., Frye R. A., Pandita T. K., Guarente L., Weinberg R. A. (2001) Cell 107, 149–159 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

