Detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus (HCV) by MultiCode-RTx real-time PCR targeting the HCV 3' untranslated region
- PMID: 19535519
- PMCID: PMC2725663
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02170-08
Detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus (HCV) by MultiCode-RTx real-time PCR targeting the HCV 3' untranslated region
Abstract
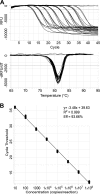
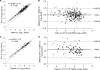
A prototype, real-time reverse-transcription PCR assay, based on MultiCode-RTx technology, quantifying hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA by targeting the HCV 3' untranslated region demonstrated linearity over 7 logs, with a good correlation between the quantitative results of this assay and the results of two commercially available comparator assays for 466 clinical specimens comprising all six HCV genotypes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Performance characteristics of the MultiCode-RTx hepatitis C virus load test targeting the 3' untranslated region.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 May;48(5):1771-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00142-10. Epub 2010 Mar 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20335413 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a low-cost real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction technique for the detection and quantification of hepatitis C viral load.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010 Jun;48(6):777-84. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2010.134. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010. PMID: 20218905
-
Development and validation of an RT-qPCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA for routine testing in Moroccan clinical specimens.J Med Virol. 2019 Mar;91(3):428-436. doi: 10.1002/jmv.25326. Epub 2018 Oct 28. J Med Virol. 2019. PMID: 30267578
-
Virological tools to diagnose and monitor hepatitis C virus infection.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011 Feb;17(2):116-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2010.03418.x. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2011. PMID: 21054664 Review.
-
Use and interpretation of hepatitis C virus diagnostic assays.Clin Liver Dis. 2003 Feb;7(1):127-37. doi: 10.1016/s1089-3261(02)00064-8. Clin Liver Dis. 2003. PMID: 12691462 Review.
Cited by
-
Performance characteristics of the MultiCode-RTx hepatitis C virus load test targeting the 3' untranslated region.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 May;48(5):1771-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00142-10. Epub 2010 Mar 24. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20335413 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibits Spread of Hepatitis C Virus Among Liver Cells, Independent From Interferons.Gastroenterology. 2017 Aug;153(2):566-578.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.021. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28456632 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation and Validation of the Roche Light Cycler 480 96-Well Plate Platform as a Real-Time PCR Assay for the Quantitative Detection of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) in Clinical Specimens Using the Luminex MultiCode ASRs System.Med Sci (Basel). 2020 Mar 11;8(1):14. doi: 10.3390/medsci8010014. Med Sci (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32168800 Free PMC article.
-
Viral genome imaging of hepatitis C virus to probe heterogeneous viral infection and responses to antiviral therapies.Virology. 2016 Jul;494:236-47. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Virology. 2016. PMID: 27128351 Free PMC article.
-
Highly sensitive and quantitative detection of the H274Y oseltamivir resistance mutation in seasonal A/H1N1 influenza virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Oct;48(10):3517-24. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01031-10. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20668122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colucci, G., J. Ferguson, C. Harkleroad, S. Lee, D. Romo, S. Soviero, J. Thompson, M. Velez, A. Wang, Y. Miyahara, S. Young, and C. Sarrazin. 2007. Improved COBAS TaqMan hepatitis C virus test (version 2.0) for use with the High Pure system: enhanced genotype inclusivity and performance characteristics in a multisite study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 453595-3600. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferreira-Gonzalez, A., M. L. Shiffman, D. H. Lofland, M. R. Langley, D. W. Gainey, and C. T. Garrett. 1996. Assessing clinical utility of hepatitis C virus quantitative RT-PCR data: implications for identification of responders among alpha-interferon-treated patients. Mol. Diagn. 1109-120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

