Reliable means of diagnosis and serovar determination of blood-borne Salmonella strains: quick PCR amplification of unique genomic loci by novel primer sets
- PMID: 19535522
- PMCID: PMC2725699
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00327-09
Reliable means of diagnosis and serovar determination of blood-borne Salmonella strains: quick PCR amplification of unique genomic loci by novel primer sets
Abstract
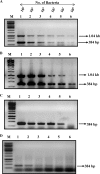
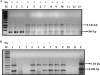
Typhoid fever is becoming an ever increasing threat in the developing countries. We have improved considerably upon the existing PCR-based diagnosis method by designing primers against a region that is unique to Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi and Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Paratyphi A, corresponding to the STY0312 gene in S. Typhi and its homolog SPA2476 in S. Paratyphi A. An additional set of primers amplify another region in S. Typhi CT18 and S. Typhi Ty2 corresponding to the region between genes STY0313 to STY0316 but which is absent in S. Paratyphi A. The possibility of a false-negative result arising due to mutation in hypervariable genes has been reduced by targeting a gene unique to typhoidal Salmonella serovars as a diagnostic marker. The amplified region has been tested for genomic stability by amplifying the region from clinical isolates of patients from various geographical locations in India, thereby showing that this region is potentially stable. These set of primers can also differentiate between S. Typhi CT18, S. Typhi Ty2, and S. Paratyphi A, which have stable deletions in this specific locus. The PCR assay designed in this study has a sensitivity of 95% compared to the Widal test which has a sensitivity of only 63%. As observed, in certain cases, the PCR assay was more sensitive than the blood culture test was, as the PCR-based detection could also detect dead bacteria.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of a novel multiplex PCR for the detection and differentiation of Salmonella enterica serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A.Res Microbiol. 2010 May;161(4):243-8. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.03.005. Epub 2010 Apr 8. Res Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20381608
-
One-step differential detection of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, serovar Paratyphi A and other Salmonella spp. by using a quadruplex real-time PCR assay.J Microbiol Methods. 2021 Apr;183:106184. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106184. Epub 2021 Mar 1. J Microbiol Methods. 2021. PMID: 33662480
-
[Taq Man probe-based quadruple real-time PCR for detection of Salmonella paratyphi A/B/C and Salmonella typhi].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2017 Mar;46(2):298-302. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2017. PMID: 29903111 Chinese.
-
Antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhi and paratyphi in South Asia-current status, issues and prospects.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015;41(4):536-45. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2014.880662. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 24645636 Review.
-
[Typhoid and paratyphoid fever].Z Gastroenterol. 2020 Feb;58(2):160-170. doi: 10.1055/a-1063-1945. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Z Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32050286 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Clinical Evaluation of a Multiplex PCR for the Detection of Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Paratyphi A from Blood Specimens in a High-Endemic Setting.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019 Sep;101(3):513-520. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0992. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2019. PMID: 31287048 Free PMC article.
-
A simplified multiplex PCR-based typing method for common Salmonella enterica serovars supported by online server-based detection system.Indian J Med Res. 2017 Aug;146(2):272-280. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1258_15. Indian J Med Res. 2017. PMID: 29265030 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Laboratory Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Antimicrobial Management of Invasive Salmonella Infections.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015 Oct;28(4):901-37. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00002-15. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26180063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Typhoid fever & vaccine development: a partially answered question.Indian J Med Res. 2012;135(2):161-9. Indian J Med Res. 2012. PMID: 22446857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Haloarchaeal gas vesicle nanoparticles displaying Salmonella antigens as a novel approach to vaccine development.Procedia Vaccinol. 2015;9:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.provac.2015.05.003. Procedia Vaccinol. 2015. PMID: 26900411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambati, S. R., G. Nath, and B. K. Das. 2007. Diagnosis of typhoid fever by polymerase chain reaction. Indian J. Pediatr. 74909-913. - PubMed
-
- Aziah, I., M. Ravichandran, and A. Ismail. 2007. Amplification of ST50 gene using dry-reagent-based polymerase chain reaction for the detection of Salmonella typhi. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 59373-377. - PubMed
-
- Bhan, M. K., R. Bahl, and S. Bhatnagar. 2005. Typhoid and paratyphoid fever. Lancet 366749-762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

