A crowdsourcing evaluation of the NIH chemical probes
- PMID: 19536101
- PMCID: PMC3596119
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio0709-441
A crowdsourcing evaluation of the NIH chemical probes
Erratum in
- Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Aug;5(8):600
Abstract
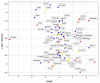
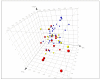
Between 2004 and 2008, the US National Institutes of Health Molecular Libraries and Imaging initiative pilot phase funded 10 high-throughput screening centers, resulting in the deposition of 691 assays into PubChem and the nomination of 64 chemical probes. We crowdsourced the Molecular Libraries and Imaging initiative output to 11 experts, who expressed medium or high levels of confidence in 48 of these 64 probes.
Figures

References
-
- Austin CP, Brady LS, Insel TR, Collins FS. Science. 2004;306:1138–1139. - PubMed
-
- [9/04/09];The PubChem database is available online at the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved from http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
-
- Hopkins AL, Polinsky A. Knowledge and Intelligence in Drug Design, Ann. Rep. Med. Chem. (41):425–437.
-
- Polanyi M. Personal Knowledge: Towards a Post-Critical Philosophy. University of Chicago Press; Chicago: 1974.
-
- Rishton GM. Drug Discov. Today. 1997;2:382–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

