Structural basis for specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains by tandem UIMs of RAP80
- PMID: 19536136
- PMCID: PMC2735169
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.160
Structural basis for specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitin chains by tandem UIMs of RAP80
Abstract
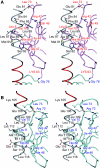
RAP80 has a key role in the recruitment of the Abraxas-BRCC36-BRCA1-BARD1 complex to DNA-damage foci for DNA repair through specific recognition of Lys 63-linked polyubiquitinated proteins by its tandem ubiquitin-interacting motifs (UIMs). Here, we report the crystal structure of the RAP80 tandem UIMs (RAP80-UIM1-UIM2) in complex with Lys 63-linked di-ubiquitin at 2.2 A resolution. The two UIMs, UIM1 and UIM2, and the alpha-helical inter-UIM region together form a continuous 60 A-long alpha-helix. UIM1 and UIM2 bind to the proximal and distal ubiquitin moieties, respectively. Both UIM1 and UIM2 of RAP80 recognize an Ile 44-centered hydrophobic patch on ubiquitin but neither UIM interacts with the Lys 63-linked isopeptide bond. Our structure suggests that the inter-UIM region forms a 12 A-long alpha-helix that ensures that the UIMs are arranged to enable specific binding of Lys 63-linked di-ubiquitin. This was confirmed by pull-down analyses using RAP80-UIM1-UIM2 mutants of various length inter-UIM regions. Further, we show that the Epsin1 tandem UIM, which has an inter-UIM region similar to that of RAP80-UIM1-UIM2, also selectively binds Lys 63-linked di-ubiquitin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Measuring ubiquitin chain linkage: Rap80 uses a molecular ruler mechanism for ubiquitin linkage specificity.EMBO J. 2009 Aug 19;28(16):2307-8. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2009.221. EMBO J. 2009. PMID: 19690555 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren GL (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D 54: 905–921 - PubMed
-
- Christensen DE, Brzovic PS, Klevit RE (2007) E2-BRCA1 RING interactions dictate synthesis of mono- or specific polyubiquitin chain linkages. Nat Struct Mol Biol 14: 941–948 - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project N (1994) The CCP4 Suite: Programs for Protein Crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D 50: 760–763 - PubMed
-
- Doil C, Mailand N, Bekker-Jensen S, Menard P, Larsen DH, Pepperkok R, Ellenberg J, Panier S, Durocher D, Bartek J, Lukas J, Lukas C (2009) RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell 136: 435–446 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

