Endocrine profile and testicular histomorphometry in adult rat offspring of diabetic mothers
- PMID: 19536612
- PMCID: PMC10717756
- DOI: 10.1007/s12576-009-0045-7
Endocrine profile and testicular histomorphometry in adult rat offspring of diabetic mothers
Abstract
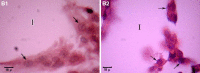
This investigation was conducted to evaluate the effect of maternal diabetes on fetal testicular structure and function, and reproductive hormones levels. Sixteen female rats were divided into two groups. Diabetes was induced in one group by alloxan. Blood was collected from 90-day-old male offspring of both groups, and the level of blood glucose, testosterone, FSH and LH in their serum was measured. Weight, volume and various histological parameters of testes were determined. A significant increase in blood glucose and decrease in LH, FSH and testosterone in sera of offspring of diabetic mothers (ODM) were observed. The weight and volume of testes in the ODM were 22.7 and 22.9% higher, respectively, than those of the control group (P < 0.05), while the ratio of testes to body weight did not change significantly. The number of seminiferous tubules increased (+21%) significantly (P < 0.05), while thickness of the testicular capsule (-25%), number of Leydig cells (-15.6%), number of Sertoli cells (-14.9%), number of spermatogonia (-26.3%) and diameter of seminiferous tubules (-11%) showed significantly reduced values in the ODM compare to the control. In conclusion, maternal hyperglycemia has a deleterious effect on testicular parameters during fetal life, which will affect reproductive endocrine during postpuberty.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Features of gonadal dysgenesis and Leydig cell impairment in testes with Sertoli cell-only syndrome.Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2020;58(2):73-82. doi: 10.5603/FHC.a2020.0008. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2020. PMID: 32490535
-
Evaluation of testis hormonal and histopathological alterations in type I and type II diabetic rats.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Oct;120(10):16775-16785. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28936. Epub 2019 May 14. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31087717
-
Classification of several types of maturational arrest of spermatogonia according to Sertoli cell morphology: an approach to aetiology.Int J Androl. 1998 Dec;21(6):317-26. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2605.1998.00122.x. Int J Androl. 1998. PMID: 9972489
-
The effects of modest intake of soy milk enriched with Lactobacillus casei and omega-3 on the testis parameters in diabetic rats: a stereological study.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Apr;57(4):1123-1133. doi: 10.1007/s11255-024-04243-x. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39592499
-
Effects of exogenous hormones on spermatogenesis in the male prairie dog (Cynomys ludovicianus).Anat Rec. 1998 Jan;250(1):45-61. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(199801)250:1<45::AID-AR5>3.0.CO;2-D. Anat Rec. 1998. PMID: 9458066
Cited by
-
Testosterone-mediated upregulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel in cardiomyocytes causes abbreviation of QT intervals in rats.J Physiol Sci. 2018 Nov;68(6):759-767. doi: 10.1007/s12576-017-0590-4. Epub 2018 Jan 13. J Physiol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29332211 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of male reproductive parameters in mice with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2020 Mar;47(1):20-33. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2020.00388. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2020. PMID: 32036645 Free PMC article.
-
The role of apelinergic system in metabolism and reproductive system in normal and pathological conditions: an overview.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 22;14:1193150. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1193150. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37424869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased spermatogenesis, fertility, and altered Slc2A expression in Akt1-/- and Akt2-/- testes and sperm.Reprod Sci. 2012 Jan;19(1):31-42. doi: 10.1177/1933719111424449. Reprod Sci. 2012. PMID: 22228739 Free PMC article.
-
Islet Transplantation Attenuating Testicular Injury in Type 1 Diabetic Rats Is Associated with Suppression of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation via Nrf-2/HO-1 and NF-κB Pathways.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Sep 5;2019:8712492. doi: 10.1155/2019/8712492. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31583254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pedersen J. The pregnant diabetic and her newborn: problems and management. 2. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1977. pp. 91–197.
-
- Persson B, Hanson U. Neonatal morbidities in gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 1998;21:79–84. - PubMed
-
- Van Assche FA, Aerts L, De Prins FA. Degranulation of the insulin-producing B cells in an infant of a diabetic mother. Case report. Br J Obstet Gynecol. 1983;90:182–185. - PubMed
-
- Knowler W, Pettitt DJ, Kunzelman CL, Everhart J. Genetic and environment determinants of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1985;1:309.
-
- Chung CS, Myrianthopoulos NC. Factors affecting risks of congenital malformations. II. Effect of maternal diabetes on congenital malformations. Birth Defects. 1975;11:23–38. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

