Nanofiber scaffolds with gradations in mineral content for mimicking the tendon-to-bone insertion site
- PMID: 19537737
- PMCID: PMC2726708
- DOI: 10.1021/nl901582f
Nanofiber scaffolds with gradations in mineral content for mimicking the tendon-to-bone insertion site
Abstract
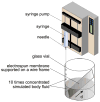
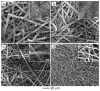
We have demonstrated a simple and versatile method for generating a continuously graded, bonelike calcium phosphate coating on a nonwoven mat of electrospun nanofibers. A linear gradient in calcium phosphate content could be achieved across the surface of the nanofiber mat. The gradient had functional consequences with regard to stiffness and biological activity. Specifically, the gradient in mineral content resulted in a gradient in the stiffness of the scaffold and further influenced the activity of mouse preosteoblast MC3T3 cells. This new class of nanofiber-based scaffolds can potentially be employed for repairing the tendon-to-bone insertion site via a tissue engineering approach.
Figures



References
-
- Barut A, Guven I, Madenci E. Int J solids struct. 2001;38:9077.
-
- Thomopoulos S, Williams GR, Gimbel JA, Favata M, Soslowsky LJ. J Orthop Res. 2003;21:413. - PubMed
-
- Zizak I, Roschger P, Paris O, Misof BM, Berzlanovich A, Bernstorff S, Amenitsch H, Klaushofer K, Fratzl P. J Struct Biol. 2003;144:208. - PubMed
- Katz JL, Misra A, Spencer P, Wang Y, Bumrerraj S, Nomura T, Eppell SJ, Tabib-Azar M. Mater Sci Eng C. 2007;27:450. - PMC - PubMed
- Wopenka B, Kent A, Pasteris JD, Yoon Y, Thomopoulos S. Appl Spectrosc. 2008;62:1285. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomopoulos S, Williams GR, Soslowsky LJ. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125:106. - PubMed
-
- Galatz LM, Silva MJ, Rothermich SY, Zaegel MA, Havlioglu N, Thomopoulos S. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:2027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

