HIV testing in a high-incidence population: is antibody testing alone good enough?
- PMID: 19538088
- PMCID: PMC3361648
- DOI: 10.1086/600043
HIV testing in a high-incidence population: is antibody testing alone good enough?
Abstract
Background: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recently recommended the expansion of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) antibody testing. However, antibody tests have longer "window periods" after HIV acquisition than do nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs).
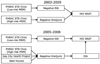
Methods: Public Health-Seattle & King County offered HIV antibody testing to men who have sex with men (MSM) using the OraQuick Advance Rapid HIV-1/2 Antibody Test (OraQuick; OraSure Technologies) on oral fluid or finger-stick blood specimens or using a first- or second-generation enzyme immunoassay. The enzyme immunoassay was also used to confirm reactive rapid test results and to screen specimens from OraQuick-negative MSM prior to pooling for HIV NAAT. Serum specimens obtained from subsets of HIV-infected persons were retrospectively evaluated by use of other HIV tests, including a fourth-generation antigen-antibody combination assay.
Results: From September 2003 through June 2008, a total of 328 (2.3%) of 14,005 specimens were HIV antibody positive, and 36 (0.3%) of 13,677 antibody-negative specimens were NAAT positive (indicating acute HIV infection). Among 6811 specimens obtained from MSM who were initially screened by rapid testing, OraQuick detected only 153 (91%) of 169 antibody-positive MSM and 80% of the 192 HIV-infected MSM detected by the HIV NAAT program. HIV was detected in serum samples obtained from 15 of 16 MSM with acute HIV infection that were retrospectively tested using the antigen-antibody combination assay.
Conclusions: OraQuick may be less sensitive than enzyme immunoassays during early HIV infection. NAAT should be integrated into HIV testing programs that serve populations that undergo frequent testing and that have high rates of HIV acquisition, particularly if rapid HIV antibody testing is employed. Antigen-antibody combination assays may be a reasonably sensitive alternative to HIV NAAT.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Branson BM, Handsfield HH, Lampe MA, Janssen RS, Taylor AW, Lyss SB, Clark JE. Revised recommendations for HIV testing of adults, adolescents, and pregnant women in health-care settings. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006;55:1–17. quiz CE11–14. - PubMed
-
- Marks G, Crepaz N, Janssen RS. Estimating sexual transmission of HIV from persons aware and unaware that they are infected with the virus in the USA. AIDS. 2006;20:1447–1450. - PubMed
-
- Wawer MJ, Gray RH, Sewankambo NK, et al. Rates of HIV-1 transmission per coital act, by stage of HIV-1 infection, in Rakai, Uganda. J Infect Dis. 2005;191:1403–1409. - PubMed
-
- Stekler J, Maenza J, Stevens CE, et al. Screening for acute HIV infection: lessons learned. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:459–461. - PubMed
-
- Fiebig EW, Wright DJ, Rawal BD, et al. Dynamics of HIV viremia and antibody seroconversion in plasma donors: implications for diagnosis and staging of primary HIV infection. AIDS. 2003;17:1871–1879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

