Cross-talk between calcineurin/NFAT and Jak/STAT signalling induces cardioprotective alphaB-crystallin gene expression in response to hypertrophic stimuli
- PMID: 19538478
- PMCID: PMC3829032
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00804.x
Cross-talk between calcineurin/NFAT and Jak/STAT signalling induces cardioprotective alphaB-crystallin gene expression in response to hypertrophic stimuli
Abstract
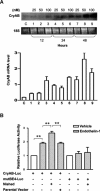
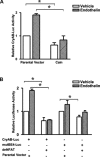
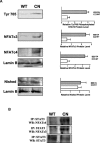
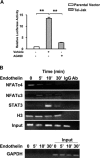
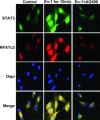
Among the stress proteins that are up-regulated in the heart due to imposed biomechanical stress, alphaB-crystallin (CryAB) is the most abundant and pivotal in rendering protection against stress-induced cell damage. Cardiomyocyte-specific expression of the CryAB gene was shown to be dependent upon an intact alphaBE4 cis-element located in the CryAB enhancer. To date, there is no evidence on the identity of regulatory proteins and associated signalling molecules that control CryAB expression in cardiomyocytes. In this study, we define a mechanism by which the calcineurin/NFAT and Jak/STAT pathways regulate CryAB gene expression in response to a hypertrophic agonist endothelin-1 (En-1), in hypertrophic hearts of mice with pressure overload (TAC) and in heart-targeted calcineurin over-expressing mice (MHC-CnA). We observed that in response to various hypertrophic stimuli the transcription factors NFAT, Nished and STAT3 form a dynamic ternary complex and interact with the alphaBE4 promoter element of the CryAB gene. Both dominant negative NFAT and AG490, an inhibitor of the Jak2 phosphorylation, inhibited CryAB gene transcription in transient transfection assays. AG490 was also effective in blocking the nuclear translocation of NFAT and STAT3 in cardiomyocytes treated with En-1. We observed a marked increase in CryAB gene expression in MHC-CnA mouse hearts accompanied with increased phosphorylation of STAT3. We conclude that hypertrophy-dependent CryAB gene expression can be attributed to a functional linkage between the Jak/STAT and calcineurin/NFAT signalling pathways, each of which are otherwise known to be involved independently in the deleterious outcome in cardiac hypertrophy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PICOT attenuates cardiac hypertrophy by disrupting calcineurin-NFAT signaling.Circ Res. 2008 Mar 28;102(6):711-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.165985. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18258855
-
Enhanced expression of DYRK1A in cardiomyocytes inhibits acute NFAT activation but does not prevent hypertrophy in vivo.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jun 1;90(3):521-8. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr023. Epub 2011 Jan 27. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21273244
-
Alpha B-crystallin suppresses pressure overload cardiac hypertrophy.Circ Res. 2008 Dec 5;103(12):1473-82. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.180117. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18974385 Free PMC article.
-
Calcineurin-NFAT signaling regulates the cardiac hypertrophic response in coordination with the MAPKs.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 Aug 15;63(3):467-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.01.021. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15276472 Review.
-
Calcineurin regulation of cytoskeleton organization: a new paradigm to analyse the effects of calcineurin inhibitors on the kidney.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Feb;16(2):218-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01398.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21801302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenomic model of cardiac enhancers with application to genome wide association studies.Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013:92-102. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013. PMID: 23424115 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy is associated with enhanced mitochondrial fission.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;454(1-2):33-44. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3450-5. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30251118
-
JAK-Inhibitors for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Focus on the Present and an Outlook on the Future.Biomolecules. 2020 Jul 5;10(7):1002. doi: 10.3390/biom10071002. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32635659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The JAK-STAT pathway in hypertrophic stress signaling and genomic stress response.JAKSTAT. 2012 Apr 1;1(2):131-41. doi: 10.4161/jkst.20702. JAKSTAT. 2012. PMID: 24058762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy response requires janus kinase 2-histone deacetylase 2 signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Nov 5;15(11):20240-53. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120240. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25380525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamradt MC, Chen F, Cryns VL. The small heat shock protein alpha B-crystallin negatively regulates cytochrome c- and caspase-8-dependent activation of caspase-3 by inhibiting its autoproteolytic maturation. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:16059–63. - PubMed
-
- Kamradt MC, Lu M, Werner ME, Kwan T, et al. The small heat shock protein alpha B-crystallin is a novel inhibitor of TRAIL-induced apoptosis that suppresses the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:11059–66. - PubMed
-
- Golenhofen N, Ness W, Koob R, et al. Ischemia-induced phosphorylation and translocation of stress protein alpha B-crystallin to Z lines of myocardium. Am J Physiol. 1998;274:H1457–64. - PubMed
-
- Bullard B, Ferguson C, Minajeva A, et al. Association of the chaperone alphaB-crystallin with titin in heart muscle. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:7917–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

