Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in fasting-mediated oxidative stress
- PMID: 19539749
- PMCID: PMC2759705
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.06.017
Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in fasting-mediated oxidative stress
Abstract
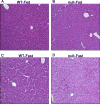
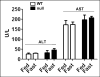
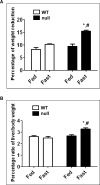
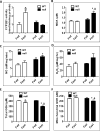
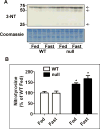
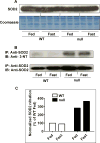
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) regulates lipid homeostasis, particularly in the liver. This study was aimed at elucidating the relationship between hepatosteatosis and oxidative stress during fasting. Fasted Ppara-null mice exhibited marked hepatosteatosis, which was associated with elevated levels of lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide synthase activity, and hydrogen peroxide accumulation. Total glutathione (GSH), mitochondrial GSH, and the activities of major antioxidant enzymes were also lower in the fasted Ppara-null mice. Consequently, the number and extent of nitrated proteins were markedly increased in the fasted Ppara-null mice, although high levels of protein nitration were still detected in the fed Ppara-null mice while many oxidatively modified proteins were only found in the fasted Ppara-null mice. However, the role of inflammation in increased oxidative stress in the fasted Ppara-null mice was minimal based on the similar levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha change in all groups. These results with increased oxidative stress observed in the fasted Ppara-null mice compared with other groups demonstrate a role for PPAR alpha in fasting-mediated oxidative stress and that inhibition of PPAR alpha functions may increase the susceptibility to oxidative damage in the presence of another toxic agent.
Figures




References
-
- Braissant O, Foufelle F, Scotto C, Dauca M, Wahli W. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs): tissue distribution of PPAR-alpha, -beta, and -gamma in the adult rat. Endocrinology. 1996;137:354–366. - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:649–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

