Computational selection of inhibitors of Abeta aggregation and neuronal toxicity
- PMID: 19540126
- PMCID: PMC2743868
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.05.047
Computational selection of inhibitors of Abeta aggregation and neuronal toxicity
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the cerebral accumulation of misfolded and aggregated amyloid-beta protein (Abeta). Disease symptoms can be alleviated, in vitro and in vivo, by 'beta-sheet breaker' pentapeptides that reduce plaque load. However the peptide nature of these compounds, made them biologically unstable and unable to penetrate membranes with high efficiency. The main goal of this study was to use computational methods to identify small molecule mimetics with better drug-like properties. For this purpose, the docked conformations of the active peptides were used to identify compounds with similar activities. A series of related beta-sheet breaker peptides were docked to solid state NMR structures of a fibrillar form of Abeta. The lowest energy conformations of the active peptides were used to design three dimensional (3D)-pharmacophores, suitable for screening the NCI database with Unity. Small molecular weight compounds with physicochemical features and a conformation similar to the active peptides were selected, ranked by docking and biochemical parameters. Of 16 diverse compounds selected for experimental screening, 2 prevented and reversed Abeta aggregation at 2-3microM concentration, as measured by Thioflavin T (ThT) fluorescence and ELISA assays. They also prevented the toxic effects of aggregated Abeta on neuroblastoma cells. Their low molecular weight and aqueous solubility makes them promising lead compounds for treating AD.
Figures
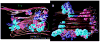
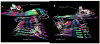
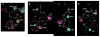


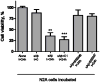
References
-
- Hendrie HC. Epidemiology of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1998;6:S3–18. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer A, Stelzmann RA, Schnitzlein HN, Murtagh FR. An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat. 1995;8(6):429–431. - PubMed
-
- Thal DR, Rub U, Orantes M, Braak H. Phases of A beta-deposition in the human brain and its relevance for the development of AD. Neurology. 2002;58(12):1791–1800. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Staging of Alzheimer’s disease-related neurofibrillary changes. Neurobiol Aging. 1995;16(3):271–278. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Toward a comprehensive theory for Alzheimer’s disease. Hypothesis: Alzheimer’s disease is caused by the cerebral accumulation and cytotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;924:17–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

