Lmx1a maintains proper neurogenic, sensory, and non-sensory domains in the mammalian inner ear
- PMID: 19540218
- PMCID: PMC3400700
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.06.016
Lmx1a maintains proper neurogenic, sensory, and non-sensory domains in the mammalian inner ear
Abstract
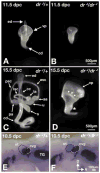
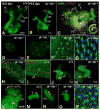
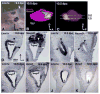
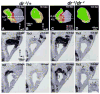
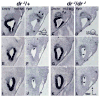
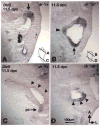
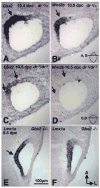
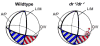
Lmx1a is a LIM homeodomain-containing transcription factor, which is required for the formation of multiple organs. Lmx1a is broadly expressed in early stages of the developing inner ear, but its expression is soon restricted to the non-sensory regions of the developing ear. In an Lmx1a functional null mutant, dreher (dr(J)/dr(J)), the inner ears lack a non-sensory structure, the endolymphatic duct, and the membranous labyrinth is poorly developed. These phenotypes are consistent with Lmx1a's role as a selector gene. More importantly, while all three primary fates of the inner ear - neural, sensory, and non-sensory - are specified in dr(J)/dr(J), normal boundaries among these tissues are often violated. For example, the neurogenic domain of the ear epithelium, from which cells delaminate to form the cochleovestibular ganglion, is expanded. Within the neurogenic domain, the demarcation between the vestibular and auditory neurogenic domains is most likely disrupted as well, based on the increased numbers of vestibular neuroblasts and ectopic expression of Fgf3, which normally is associated specifically with the vestibular neurogenic region. Furthermore, aberrant and ectopic sensory organs are observed; most striking among these is vestibular-like hair cells located in the cochlear duct.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lmx1a is required for segregation of sensory epithelia and normal ear histogenesis and morphogenesis.Cell Tissue Res. 2008 Dec;334(3):339-58. doi: 10.1007/s00441-008-0709-2. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Cell Tissue Res. 2008. PMID: 18985389 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal Negative Regulation Between Lmx1a and Lmo4 Is Required for Inner Ear Formation.J Neurosci. 2018 Jun 6;38(23):5429-5440. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2484-17.2018. Epub 2018 May 16. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29769265 Free PMC article.
-
Forced activation of Wnt signaling alters morphogenesis and sensory organ identity in the chicken inner ear.Dev Biol. 2003 Sep 1;261(1):149-64. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00297-5. Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 12941626
-
Inner ear development: building a spiral ganglion and an organ of Corti out of unspecified ectoderm.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jul;361(1):7-24. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2031-5. Epub 2014 Nov 9. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25381571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling regulating inner ear development: cell fate determination, patterning, morphogenesis, and defects.Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2015 Feb;55(1):17-25. doi: 10.1111/cga.12072. Congenit Anom (Kyoto). 2015. PMID: 25040109 Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond generalized hair cells: molecular cues for hair cell types.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.008. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23201032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of inner ear development.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012 Aug 1;4(8):a008409. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a008409. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012. PMID: 22855724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterozygous missense variants of LMX1A lead to nonsyndromic hearing impairment and vestibular dysfunction.Hum Genet. 2018 May;137(5):389-400. doi: 10.1007/s00439-018-1880-5. Epub 2018 May 12. Hum Genet. 2018. PMID: 29754270 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and development of the tetrapod auditory system: an organ of Corti-centric perspective.Evol Dev. 2013 Jan;15(1):63-79. doi: 10.1111/ede.12015. Evol Dev. 2013. PMID: 23331918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The acquisition of positional information across the radial axis of the cochlea.Dev Dyn. 2020 Mar;249(3):281-297. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.118. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Dev Dyn. 2020. PMID: 31566832 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anagnostopoulos AV. A compendium of mouse knockouts with inner ear defects. Trends Genet. 2002;18:499. - PubMed
-
- Arques CG, Doohan R, Sharpe J, Torres M. Cell tracing reveals a dorsoventral lineage restriction plane in the mouse limb bud mesenchyme. Development. 2007;134:3713–22. - PubMed
-
- Bell D, Streit A, Gorospe I, Varela-Nieto I, Alsina B, Giraldez F. Spatial and temporal segregation of auditory and vestibular neurons in the otic placode. Dev Biol. 2008;322:109–20. - PubMed
-
- Bok J, Chang W, Wu DK. Patterning and morphogenesis of the vertebrate inner ear. Int J Dev Biol. 2007a;51:521–33. - PubMed
-
- Bok J, Dolson DK, Hill P, Ruther U, Epstein DJ, Wu DK. Opposing gradients of Gli repressor and activators mediate Shh signaling along the dorsoventral axis of the inner ear. Development. 2007b;134:1713–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

