mTOR and HIF-1alpha-mediated tumor metabolism in an LKB1 mouse model of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- PMID: 19541609
- PMCID: PMC2708689
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0900465106
mTOR and HIF-1alpha-mediated tumor metabolism in an LKB1 mouse model of Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Abstract
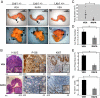
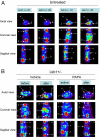
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) is a familial cancer disorder due to inherited loss of function mutations in the LKB1/ STK11 serine/threonine kinase. PJS patients develop gastrointestinal hamartomas with 100% penetrance often in the second decade of life, and demonstrate an increased predisposition toward the development of a number of additional malignancies. Among mitogenic signaling pathways, the mammalian-target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway is hyperactivated in tissues and tumors derived from LKB1-deficient mice. Consistent with a central role for mTORC1 in these tumors, rapamycin as a single agent results in a dramatic suppression of preexisting GI polyps in LKB1+/- mice. However, the key targets of mTORC1 in LKB1-deficient tumors remain unknown. We demonstrate here that these polyps, and LKB1- and AMPK-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts, show dramatic up-regulation of the HIF-1alpha transcription factor and its downstream transcriptional targets in an rapamycin-suppressible manner. The HIF-1alpha targets hexokinase II and Glut1 are up-regulated in these polyps, and using FDG-PET, we demonstrate that LKB1+/- mice show increased glucose utilization in focal regions of their GI tract corresponding to these gastrointestinal hamartomas. Importantly, we demonstrate that polyps from human Peutz-Jeghers patients similarly exhibit up-regulated mTORC1 signaling, HIF-1alpha, and GLUT1 levels. Furthermore, like HIF-1alpha and its target genes, the FDG-PET signal in the GI tract of these mice is abolished by rapamycin treatment. These findings suggest a number of therapeutic modalities for the treatment and detection of hamartomas in PJS patients, and potential for the screening and treatment of the 30% of sporadic human lung cancers bearing LKB1 mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Loss of the tumor suppressor LKB1 promotes metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells via HIF-1α.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):2554-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312570111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550282 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Peutz-Jeghers polyposis by targeting mammalian target of rapamycin signaling.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Feb 15;14(4):1167-71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4007. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18281551
-
Stromal liver kinase B1 [STK11] signaling loss induces oviductal adenomas and endometrial cancer by activating mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(8):e1002906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002906. Epub 2012 Aug 16. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22916036 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Serine/Threonine Kinase 11 (STK11) or Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1) Gene in Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020;30(3):245-252. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2020033451. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2020. PMID: 32749111 Review.
-
Dysregulation of HIF and VEGF is a unifying feature of the familial hamartoma syndromes.Cancer Cell. 2004 Jul;6(1):7-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2004.06.020. Cancer Cell. 2004. PMID: 15261137 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between HIFs and tumor immune checkpoints: mechanism and therapy.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00836-7. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38165484 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium-glucose transporter 2 is a diagnostic and therapeutic target for early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Transl Med. 2018 Nov 14;10(467):eaat5933. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat5933. Sci Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30429355 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine Monophosphate Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) enhances chemotherapy response in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).Cancer Lett. 2022 Jun 1;535:215659. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215659. Epub 2022 Mar 20. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35321842 Free PMC article.
-
Tubular injury in a rat model of type 2 diabetes is prevented by metformin: a possible role of HIF-1α expression and oxygen metabolism.Diabetes. 2011 Mar;60(3):981-92. doi: 10.2337/db10-0655. Epub 2011 Jan 31. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21282369 Free PMC article.
-
Heightening Energetic Stress Selectively Targets LKB1-Deficient Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers.Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;75(22):4910-22. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0797. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26574479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez-Cespedes M, et al. Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event in adenocarcinomas of the lung. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3659–3662. - PubMed
-
- Carretero J, Medina PP, Pio R, Montuenga LM, Sanchez-Cespedes M. Novel and natural knockout lung cancer cell lines for the LKB1/STK11 tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene. 2004;23:4037–4040. - PubMed
-
- Ji H, et al. LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature. 2007;448:807–810. - PubMed
-
- Hemminki A, et al. A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature. 1998;391:184–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

