NAADP-mediated Ca2+ signaling via type 1 ryanodine receptor in T cells revealed by a synthetic NAADP antagonist
- PMID: 19541638
- PMCID: PMC2697110
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809997106
NAADP-mediated Ca2+ signaling via type 1 ryanodine receptor in T cells revealed by a synthetic NAADP antagonist
Abstract
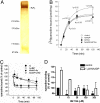
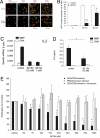
The nucleotide NAADP was recently discovered as a second messenger involved in the initiation and propagation of Ca(2+) signaling in lymphoma T cells, but its impact on primary T cell function is still unknown. An optimized, synthetic, small molecule inhibitor of NAADP action, termed BZ194, was designed and synthesized. BZ194 neither interfered with Ca(2+) mobilization by d-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate or cyclic ADP-ribose nor with capacitative Ca(2+) entry. BZ194 specifically and effectively blocked NAADP-stimulated [(3)H]ryanodine binding to the purified type 1 ryanodine receptor. Further, in intact T cells, Ca(2+) mobilization evoked by NAADP or by formation of the immunological synapse between primary effector T cells and astrocytes was inhibited by BZ194. Downstream events of Ca(2+) mobilization, such as nuclear translocation of "nuclear factor of activated T cells" (NFAT), T cell receptor-driven interleukin-2 production, and proliferation in antigen-experienced CD4(+) effector T cells, were attenuated by the NAADP antagonist. Taken together, specific inhibition of the NAADP signaling pathway constitutes a way to specifically and effectively modulate T-cell activation and has potential in the therapy of autoimmune diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
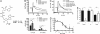

Similar articles
-
Ca2+ release via ryanodine receptors and Ca2+ entry: major mechanisms in NAADP-mediated Ca2+ signaling in T-lymphocytes.Cell Signal. 2004 Nov;16(11):1283-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2004.03.013. Cell Signal. 2004. PMID: 15337527
-
Frontrunners of T cell activation: Initial, localized Ca2+ signals mediated by NAADP and the type 1 ryanodine receptor.Sci Signal. 2015 Oct 13;8(398):ra102. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aab0863. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26462735
-
Functional ryanodine receptor expression is required for NAADP-mediated local Ca2+ signaling in T-lymphocytes.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21394-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413085200. Epub 2005 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15774471
-
Ca(2+) microdomains, NAADP and type 1 ryanodine receptor in cell activation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jun;1863(6 Pt B):1379-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.01.014. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26804481 Review.
-
Cyclic ADP-ribose and NAADP: fraternal twin messengers for calcium signaling.Sci China Life Sci. 2011 Aug;54(8):699-711. doi: 10.1007/s11427-011-4197-3. Epub 2011 Jul 24. Sci China Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21786193 Review.
Cited by
-
Essential requirement for JPT2 in NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signaling.Sci Signal. 2021 Mar 23;14(675):eabd5605. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abd5605. Sci Signal. 2021. PMID: 33758061 Free PMC article.
-
Two-pore channels: going with the flows.Biochem Soc Trans. 2022 Aug 31;50(4):1143-1155. doi: 10.1042/BST20220229. Biochem Soc Trans. 2022. PMID: 35959977 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate analogues containing substituted nicotinic acid: effect of modification on Ca(2+) release.J Med Chem. 2010 Nov 11;53(21):7599-612. doi: 10.1021/jm1007209. J Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20942470 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) degradation by alkaline phosphatase.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 21;287(39):32525-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.362715. Epub 2012 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22851169 Free PMC article.
-
P2X4 and P2X7 are essential players in basal T cell activity and Ca2+ signaling milliseconds after T cell activation.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 4;8(5):eabl9770. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl9770. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35119925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feske S, et al. A mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC channel function. Nature. 2006;441:179–185. - PubMed
-
- Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983;306:67–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

