Activation of tumor cell integrin alphavbeta3 controls angiogenesis and metastatic growth in the brain
- PMID: 19541645
- PMCID: PMC2697113
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903035106
Activation of tumor cell integrin alphavbeta3 controls angiogenesis and metastatic growth in the brain
Abstract
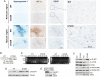
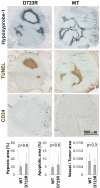
The incidence of brain metastasis is rising and poses a severe clinical problem, as we lack effective therapies and knowledge of mechanisms that control metastatic growth in the brain. Here we demonstrate a crucial role for high-affinity tumor cell integrin alpha(v)beta(3) in brain metastatic growth and recruitment of blood vessels. Although alpha(v)beta(3) is frequently up-regulated in primary brain tumors and metastatic lesions of brain homing cancers, we show that it is the alpha(v)beta(3) activation state that is critical for brain lesion growth. Activated, but not non-activated, tumor cell alpha(v)beta(3) supports efficient brain metastatic growth through continuous up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) protein under normoxic conditions. In metastatic brain lesions carrying activated alpha(v)beta(3), VEGF expression is controlled at the post-transcriptional level and involves phosphorylation and inhibition of translational respressor 4E-binding protein (4E-BP1). In contrast, tumor cells with non-activated alpha(v)beta(3) depend on hypoxia for VEGF induction, resulting in reduced angiogenesis, tumor cell apoptosis, and inefficient intracranial growth. Importantly, the microenvironment critically influences the effects that activated tumor cell alpha(v)beta(3) exerts on tumor cell growth. Although it strongly promoted intracranial growth, the activation state of the receptor did not influence tumor growth in the mammary fat pad as a primary site. Thus, we identified a mechanism by which metastatic cells thrive in the brain microenvironment and use the high-affinity form of an adhesion receptor to grow and secure host support for proliferation. Targeting this molecular mechanism could prove valuable for the inhibition of brain metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
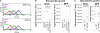


Similar articles
-
Role of host microenvironment in angiogenesis and microvascular functions in human breast cancer xenografts: mammary fat pad versus cranial tumors.Clin Cancer Res. 2002 Apr;8(4):1008-13. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11948107
-
VEGF-integrin interplay controls tumor growth and vascularization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 24;102(21):7589-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502935102. Epub 2005 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15897451 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclin A1 modulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and promotes hormone-dependent growth and angiogenesis of breast cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 8;8(8):e72210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072210. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991063 Free PMC article.
-
beta1-integrin is dispensable for the induction of ErbB2 mammary tumors but plays a critical role in the metastatic phase of tumor progression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Aug 31;107(35):15559-64. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1003034107. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20713705 Free PMC article.
-
Non-genomic Actions of Thyroid Hormones Regulate the Growth and Angiogenesis of T Cell Lymphomas.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 13;10:63. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00063. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30814977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Boosting the Potential of Chemotherapy in Advanced Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis via Micro-Combinatorial Hydrogel Particles.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Apr;10(10):e2205223. doi: 10.1002/advs.202205223. Epub 2023 Jan 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36683230 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of optical imaging agents in a fluorescence-guided surgical model of head and neck cancer.Surg Oncol. 2018 Jun;27(2):225-230. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Surg Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29937175 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of plasmalogens in post-natal retinal vascular development.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 25;9(6):e101076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101076. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24963632 Free PMC article.
-
SMI-Ribosome inactivating protein conjugates selectively inhibit tumor cell growth.Chem Commun (Camb). 2017 Apr 11;53(30):4234-4237. doi: 10.1039/c7cc00745k. Chem Commun (Camb). 2017. PMID: 28357420 Free PMC article.
-
Crossing the barrier: treatment of brain tumors using nanochain particles.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2016 Sep;8(5):678-95. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1387. Epub 2016 Jan 9. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26749497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ranasinghe MG, Sheehan JM. Surgical management of brain metastases. Neurosurg Focus. 2007;22:E2. - PubMed
-
- Lin NU, Bellon JR, Winer EP. CNS metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3608–3617. - PubMed
-
- Arias-Salgado EG, Lizano S, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH. Specification of the direction of adhesive signaling by the integrin beta cytoplasmic domain. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:29699–29707. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg MH, Partridge A, Shattil SJ. Integrin regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:509–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

