Adenosine A2A receptor is a unique angiogenic target of HIF-2alpha in pulmonary endothelial cells
- PMID: 19541651
- PMCID: PMC2705563
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0901326106
Adenosine A2A receptor is a unique angiogenic target of HIF-2alpha in pulmonary endothelial cells
Abstract
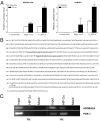
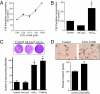
Hypoxia, through the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha (HIFs), induces angiogenesis by up-regulating a common set of angiogenic cytokines. Unlike HIF-1alpha, which regulates a unique set of genes, most genes regulated by HIF-2alpha overlap with those induced by HIF-1alpha. Thus, the unique contribution of HIF-2alpha remains largely obscure. By using adenoviral mutant HIF-1alpha and adenoviral mutant HIF-2alpha constructs, where the HIFs are transcriptionally active under normoxic conditions, we show that HIF-2alpha but not HIF-1alpha regulates adenosine A(2A) receptor in primary cultures of human lung endothelial cells. Further, siRNA knockdown of HIF-2alpha completely inhibits hypoxic induction of A(2A) receptor. Promoter studies show a 2.5-fold induction of luciferase activity with HIF-2alpha cotransfection. Analysis of the A(2A) receptor gene promoter revealed a hypoxia-responsive element in the region between -704 and -595 upstream of the transcription start site. By using a ChIP assay, we demonstrate that HIF-2alpha binding to this region is specific. In addition, we demonstrate that A(2A) receptor has angiogenic potential, as assessed by increases in cell proliferation, cell migration, and tube formation. Additional data show increased expression of A(2A) receptor in human lung tumor cancer samples relative to adjacent normal lung tissue. These data also demonstrate that A(2A) receptor is regulated by hypoxia and HIF-2alpha in human lung endothelial cells but not in mouse-derived endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: National Jewish Health, A.A. and C.W.W. hold a pending patent on use of adenosine A2A receptor as a marker of HIF-2α activation in various disease states.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in varicose veins.J Vasc Surg. 2012 May;55(5):1427-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.111. Epub 2012 Jan 24. J Vasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22277691
-
Differential regulation of pulmonary vascular cell growth by hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1α and hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-2α.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Jul;49(1):78-85. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0107OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23492195 Free PMC article.
-
Opposite functions of HIF-α isoforms in VEGF induction by TGF-β1 under non-hypoxic conditions.Oncogene. 2011 Mar 10;30(10):1213-28. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.498. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Oncogene. 2011. PMID: 21057546
-
The Distinct Role of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in Hypoxia and Angiogenesis.Cells. 2025 May 4;14(9):673. doi: 10.3390/cells14090673. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40358197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the HIF switch in human endothelial and cancer cells.Eur J Cell Biol. 2024 Jun;103(2):151386. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2024.151386. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Eur J Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38262137 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia and HIF Signaling: One Axis with Divergent Effects.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 5;21(16):5611. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165611. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32764403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenosine receptors as drug targets--what are the challenges?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013 Apr;12(4):265-86. doi: 10.1038/nrd3955. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23535933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Culture of Cancer Cells at Physiological Oxygen Levels Affects Gene Expression in a Cell-Type Specific Manner.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 14;12(11):1684. doi: 10.3390/biom12111684. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36421698 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced and calpain-dependent cleavage of filamin A regulates the hypoxic response.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 18;111(7):2560-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320815111. Epub 2014 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24550283 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the adenosinergic pathway: the indispensable part of oncological therapy in the future.Purinergic Signal. 2019 Mar;15(1):53-67. doi: 10.1007/s11302-018-9641-4. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Purinergic Signal. 2019. PMID: 30809739 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Semenza GL. Regulation of physiological responses to continuous and intermittent hypoxia by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Exp Physiol. 2006;91:803–806. - PubMed
-
- Giatromanolaki A, Sivridis E, Fiska A, Koukourakis MI. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha (HIF-2 alpha) induces angiogenesis in breast carcinomas. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2006;14:78–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL084376/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL56263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001080/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL056263/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL084923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R29 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL084376/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL60569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K12-KL2RR025779/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025779/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL060569/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK050189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK50189/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

