Endothelium-specific overexpression of human IC53 downregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and elevates systolic blood pressure in mice
- PMID: 19541669
- PMCID: PMC6279175
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvp204
Endothelium-specific overexpression of human IC53 downregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and elevates systolic blood pressure in mice
Abstract
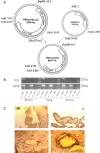
Aims: Hypertension is one of the major risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Endothelial cells (ECs) exert important functions in the regulation of blood pressure. A novel gene, IC53, as an isoform of the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)-binding protein gene C53, is mainly expressed in vascular ECs and is upregulated in the failing heart of rats. Overexpression of IC53 promotes proliferation of ECs. To examine whether IC53 plays a role in the regulation of vascular tone and blood pressure, we constructed a transgenic (tg) mouse model of the IC53 gene and studied its phenotypes relevant to vascular function.
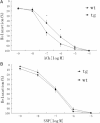
Methods and results: IC53 cDNA was cloned from a human aorta cDNA library. Using the endothelium-specific VE-cadherin promoter, we constructed tg mice in which IC53 was specifically overexpressed in vascular endothelia and found that the tg mice exhibit elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) in contrast to the wild-type (wt) controls. Further studies revealed impaired endothelium-dependent vasodilation, reduced nitric oxide (NO) production and decreased endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) expression, and activity in the tg mice. Inhibition of IC53 in human umbilical vein ECs induces upregulation of eNOS activity.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that IC53 participates in the regulation of vascular homeostasis. Endothelium-specific overexpression of IC53 is associated with elevated SBP, which may be in part attributed to the downregulation of eNOS signalling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
VE-PTP inhibition elicits eNOS phosphorylation to blunt endothelial dysfunction and hypertension in diabetes.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 May 25;117(6):1546-1556. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa213. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 32653904 Clinical Trial.
-
Rap1b in smooth muscle and endothelium is required for maintenance of vascular tone and normal blood pressure.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Jul;34(7):1486-94. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303678. Epub 2014 May 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24790136 Free PMC article.
-
Vasomotor control in mice overexpressing human endothelial nitric oxide synthase.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):H1144-53. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00773.2006. Epub 2007 May 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17496213
-
Alterations in endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity and their relevance to blood pressure.Biochem Pharmacol. 2022 Nov;205:115256. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115256. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36185001 Review.
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase transgenic models of endothelial dysfunction.Pflugers Arch. 2010 Nov;460(6):965-74. doi: 10.1007/s00424-010-0867-4. Epub 2010 Aug 10. Pflugers Arch. 2010. PMID: 20697735 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An updated meta-analysis of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene: three well-characterized polymorphisms with hypertension.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24266. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024266. Epub 2011 Sep 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21912683 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying susceptibility genes for essential hypertension by transcriptome-wide association study.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022 Nov 21;32:101387. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2022.101387. eCollection 2022 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2022. PMID: 36438602 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Determinants of Cardiovascular Disease: The Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase 3 (eNOS3), Krüppel-Like Factor-14 (KLF-14), Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR), MiRNAs27a and Their Association with the Predisposition and Susceptibility to Coronary Artery Disease.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;12(11):1905. doi: 10.3390/life12111905. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36431040 Free PMC article.
-
Association between eNOS rs1799983 polymorphism and hypertension: a meta-analysis involving 14,185 cases and 13,407 controls.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Aug 9;21(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02192-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 34372765 Free PMC article.
-
Limited clinical utility for GWAS or polygenic risk score for postoperative acute kidney injury in non-cardiac surgery in European-ancestry patients.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Oct 21;23(1):339. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-02964-8. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36271344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rutan GH, Kuller LH, Neaton JD, Wentworth DN, McDonald RH, Smith WM. Mortality associated with diastolic hypertension and isolated systolic hypertension among men screened for the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Circulation. 1988;77:504–514. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenstein MJ. Isolated systolic hypertension: how common? How risky? South Med J. 1985;78:972–978. - PubMed
-
- Nadar S, Blann AD, Lip GY. Endothelial dysfunction: methods of assessment and application to hypertension. Curr Pharm Des. 2004;10:3591–3605. - PubMed
-
- Fang ZY, Marwick TH. Vascular dysfunction and heart failure: epiphenomenon or etiologic agent? Am Heart J. 2002;143:383–390. - PubMed
-
- Ching YP, Qi Z, Wang JH. Cloning of three novel neuronal Cdk5 activator binding proteins. Gene. 2000;242:285–294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

