Minireview: Pref-1: role in adipogenesis and mesenchymal cell fate
- PMID: 19541743
- PMCID: PMC2775937
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0160
Minireview: Pref-1: role in adipogenesis and mesenchymal cell fate
Abstract
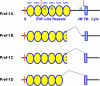
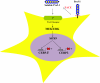
Preadipocyte factor-1 [Pref-1; also called Dlk1 (Delta-like protein 1)] is made as an epidermal growth factor-repeat containing transmembrane protein that produces a biologically active soluble form by TNF-alpha-converting enzyme (TACE)-mediated cleavage. Soluble Pref-1 activates the MAPK kinase/ERK pathway. In adipose tissue, Pref-1 is specifically expressed in preadipocytes but not in adipocytes and thus is used as a preadipocyte marker. Inhibition of adipogenesis by Pref-1 has been well established in vitro as well as in vivo by ablation and overexpression of Pref-1. SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 9 (Sox9), a transcription factor expressed in preadipocytes to suppress CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta and (C/EBP) delta expression, is required to be down-regulated before adipocyte differentiation can proceed. By activating MAPK kinase/ERK, Pref-1 prevents down-regulation of Sox9, resulting in inhibition of adipogenesis. Furthermore, by inducing Sox9, Pref-1 promotes chondrogenic induction of mesenchymal cells but prevents chondrocyte maturation as well as osteoblast differentiation. Thus, Pref-1 directs multipotent mesenchymal cells toward the chondrogenic lineage but inhibits differentiation into adipocytes as well as osteoblasts and chondrocytes. Pref-1, encoded by an imprinted gene, has also been detected in progenitor cells in various tissues during regeneration and therefore may have a more general role in maintaining cells in an undifferentiated state.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pref-1 regulates mesenchymal cell commitment and differentiation through Sox9.Cell Metab. 2009 Mar;9(3):287-302. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.01.013. Cell Metab. 2009. PMID: 19254573 Free PMC article.
-
Pref-1 interacts with fibronectin to inhibit adipocyte differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jul;30(14):3480-92. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00057-10. Epub 2010 May 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20457810 Free PMC article.
-
Pref-1, a preadipocyte secreted factor that inhibits adipogenesis.J Nutr. 2006 Dec;136(12):2953-6. doi: 10.1093/jn/136.12.2953. J Nutr. 2006. PMID: 17116701
-
Function of pref-1 as an inhibitor of adipocyte differentiation.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000 Nov;24 Suppl 4:S15-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801494. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000. PMID: 11126233 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of adipocyte differentiation and inhibitory action of pref-1.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997;7(4):281-98. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v7.i4.10. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1997. PMID: 9607168 Review.
Cited by
-
Delta-like 1 (DLK1) is a possible mediator of vitamin D effects on bone and energy metabolism.Bone. 2020 Sep;138:115510. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115510. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Bone. 2020. PMID: 32622071 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Transactivation of Atg4b by C/EBPβ promotes autophagy to facilitate adipogenesis.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;33(16):3180-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00193-13. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23754749 Free PMC article.
-
Biologically anchored knowledge expansion approach uncovers KLF4 as a novel insulin signaling regulator.PLoS One. 2018 Sep 21;13(9):e0204100. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204100. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30240435 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of sortilin in affecting the metabolism of glucose and lipid profiles.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022 Jun 1;22(3):340-352. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2021.6601. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 34784266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Constitutive IKK2 activation in intestinal epithelial cells induces intestinal tumors in mice.J Clin Invest. 2011 Jul;121(7):2781-93. doi: 10.1172/JCI45349. Epub 2011 Jun 23. J Clin Invest. 2011. PMID: 21701067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Faust IM, Miller Jr WH, Sclafani A, Aravich PF, Triscari J, Sullivan AC 1984 Diet-dependent hyperplastic growth of adipose tissue in hypothalamic obese rats. Am J Physiol 247:R1038–R1046 - PubMed
-
- Miller Jr WH, Faust IM, Hirsch J 1984 Demonstration of de novo production of adipocytes in adult rats by biochemical and radioautographic techniques. J Lipid Res 25:336–347 - PubMed
-
- Kirkland JL, Hollenberg CH, Gillon WS 1990 Age, anatomic site, and the replication and differentiation of adipocyte precursors. Am J Physiol 258:C206–C210 - PubMed
-
- Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR 2007 Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell 131:242–256 - PubMed
-
- Otto TC, Lane MD 2005 Adipose development: from stem cell to adipocyte. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 40:229–242 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

