Intradialytic administration of daptomycin in end stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis
- PMID: 19541812
- PMCID: PMC2709518
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01650309
Intradialytic administration of daptomycin in end stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Infusion of intravenous antibiotics after hemodialysis (HD) may delay initiation of treatment for the next HD shift. Intradialytic administration of drugs such as vancomycin during the final hour of HD obviates these delays. Daptomycin has potent activity against Gram-positive bacteria, but the manufacturer recommends that the dose be infused after HD ends. This study determined the pharmacokinetics of intradialytically dosed daptomycin in patients with ESRD.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: This prospective crossover study compared single-dose daptomycin (6 mg/kg, 30-min intravenous infusion) pharmacokinetics administered after HD versus during the last part of HD with high-permeability (HP) and low-permeability (LP) dialyzers to seven patients who had ESRD and were on thrice-weekly HD. Serial blood samples were collected to determine daptomycin serum concentrations and protein binding. Statistical analysis was done using linear mixed model analysis.
Results: The maximum serum concentration observed with a 6 mg/kg post-HD dose was 61.1 +/- 7.6 microg/ml with a mean protein binding of 89.2%. Intradialytic daptomycin administration resulted in reduced maximum serum concentration and area under the curve values that were approximately 12 to 20% lower when administered during HD with LP dialyzers and approximately 35% lower with HP dialyzers.
Conclusions: Intradialytic daptomycin administration during the last 30 min of HD is feasible, provided that larger dosages are used to compensate for intradialytic drug loss. On the basis of our findings, intradialytic doses of approximately 7 mg/kg (LP) or approximately 9 mg/kg (HP) theoretically should be bioequivalent to 6 mg/kg infused after HD. The calculated dosages are mathematically driven and must be validated in prospective clinical trials.
Figures
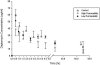
 ) versus (2) infused during the last part of HD with high-permeability (○) and (3) low-permeability (•) dialyzers to seven patients who had ESRD and were on thrice-weekly HD.
) versus (2) infused during the last part of HD with high-permeability (○) and (3) low-permeability (•) dialyzers to seven patients who had ESRD and were on thrice-weekly HD.Comment in
-
A simplified three-times weekly daptomycin dosing regimen for chronic hemodialysis patients.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010 Jan;8(1):11-4. doi: 10.1586/eri.09.121. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010. PMID: 20014897
Similar articles
-
Single-dose daptomycin pharmacokinetics in chronic haemodialysis patients.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010 Apr;25(4):1279-84. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp655. Epub 2009 Dec 10. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010. PMID: 20007981 Free PMC article.
-
Daptomycin dosing strategies in patients receiving thrice-weekly intermittent hemodialysis.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Oct;47(10):1342-7. doi: 10.1177/1060028013503110. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24259698 Review.
-
Pharmacokinetics and safety of multiple doses of daptomycin 6 mg/kg in noninfected adults undergoing hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis.Clin Nephrol. 2011 Jan;75(1):63-9. Clin Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21176752 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of 3 vancomycin dosage regimens during hemodialysis with cellulose triacetate dialyzers: post-dialysis versus intradialytic administration.Clin Nephrol. 2003 Aug;60(2):96-104. doi: 10.5414/cnp60096. Clin Nephrol. 2003. PMID: 12940611 Clinical Trial.
-
[Safety of daptomycin in patients with renal impairment].Med Clin (Barc). 2010 Dec;135 Suppl 3:55-9. doi: 10.1016/S0025-7753(10)70041-5. Med Clin (Barc). 2010. PMID: 21477705 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
High-Dose Daptomycin and Clinical Applications.Ann Pharmacother. 2021 Nov;55(11):1363-1378. doi: 10.1177/1060028021991943. Epub 2021 Feb 4. Ann Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33535792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Daptomycin pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in a pooled sample of patients receiving thrice-weekly hemodialysis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Feb;57(2):864-72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02000-12. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23208714 Free PMC article.
-
Vancomycin and daptomycin dosing recommendations in patients receiving home hemodialysis using Monte Carlo simulation.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Sep 14;24(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03314-y. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37710245 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of high-level daptomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecium during daptomycin therapy is associated with limited mutations in the bacterial genome.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013 Aug;68(8):1926-8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkt117. Epub 2013 Apr 11. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23580562 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Post-Dialysis Parenteral Antimicrobial Therapy in Patients Receiving Intermittent High-Flux Hemodialysis.Drugs. 2021 Apr;81(5):555-574. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01469-2. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33591549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pai AB, Pai MP: Optimizing antimicrobial therapy for Gram-positive bloodstream infections in patients on hemodialysis. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 13: 259–270, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Cubicin: Full Prescribing Information, Lexington, MA, Cubist Pharmaceuticals, Inc., 2008
-
- Scott MK, Macias WL, Kraus MA, Clark WR, Carfagna MA, Mueller BA: Effects of dialysis membrane on intradialytic vancomycin administration. Pharmacotherapy 17: 256–262, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Ariano RE, Fine A, Sitar DS, Rexrode S, Zelenitsky SA: Adequacy of a vancomycin dosing regimen in patients receiving high-flux hemodialysis. Am J Kidney Dis 46: 681–687, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Mason NA, Neudeck BL, Welage LS, Patel JA, Swartz RD: Comparison of 3 vancomycin dosage regimens during hemodialysis with cellulose triacetate dialyzers: Post-dialysis versus intradialytic administration. Clin Nephrol 60: 96–104, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

