Characterization of the Synechocystis strain PCC 6803 penicillin-binding proteins and cytokinetic proteins FtsQ and FtsW and their network of interactions with ZipN
- PMID: 19542290
- PMCID: PMC2725598
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00620-09
Characterization of the Synechocystis strain PCC 6803 penicillin-binding proteins and cytokinetic proteins FtsQ and FtsW and their network of interactions with ZipN
Abstract
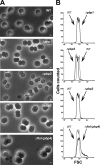
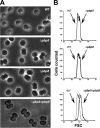
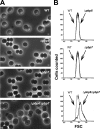
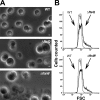
Because very little is known about cell division in noncylindrical bacteria and cyanobacteria, we investigated 10 putative cytokinetic proteins in the unicellular spherical cyanobacterium Synechocystis strain PCC 6803. Concerning the eight penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), which define three classes, we found that Synechocystis can survive in the absence of one but not two PBPs of either class A or class C, whereas the unique class B PBP (also termed FtsI) is indispensable. Furthermore, we showed that all three classes of PBPs are required for normal cell size. Similarly, the putative FtsQ and FtsW proteins appeared to be required for viability and normal cell size. We also used a suitable bacterial two-hybrid system to characterize the interaction web among the eight PBPs, FtsQ, and FtsW, as well as ZipN, the crucial FtsZ partner that occurs only in cyanobacteria and plant chloroplasts. We showed that FtsI, FtsQ, and ZipN are self-interacting proteins and that both FtsI and FtsQ interact with class A PBPs, as well as with ZipN. Collectively, these findings indicate that ZipN, in interacting with FtsZ and both FtsI and FtQ, plays a similar role to the Escherichia coli FtsA protein, which is missing in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current knowledge and recent advances in understanding metabolism of the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20193325. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193325. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32149336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ZipN, an FtsA-like orchestrator of divisome assembly in the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Oct;74(2):409-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06873.x. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19737354
-
Characterization of the FtsZ-interacting septal proteins SepF and Ftn6 in the spherical-celled cyanobacterium Synechocystis strain PCC 6803.J Bacteriol. 2009 Oct;191(19):6178-85. doi: 10.1128/JB.00723-09. Epub 2009 Jul 31. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19648234 Free PMC article.
-
FtsQ, FtsL and FtsI require FtsK, but not FtsN, for co-localization with FtsZ during Escherichia coli cell division.Mol Microbiol. 2001 Oct;42(2):395-413. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02640.x. Mol Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11703663
-
Molecular analysis of the key cytokinetic components of cyanobacteria: FtsZ, ZipN and MinCDE.Mol Microbiol. 2004 May;52(4):1145-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04042.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15130131
Cited by
-
Hormesis effects of amoxicillin on growth and cellular biosynthesis of Microcystis aeruginosa at different nitrogen levels.Microb Ecol. 2015 Apr;69(3):608-17. doi: 10.1007/s00248-014-0528-9. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Microb Ecol. 2015. PMID: 25388759
-
The lack of the cell division protein FtsZ induced generation of giant cells under acidic stress in cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC6803.Photosynth Res. 2021 Dec;150(1-3):343-356. doi: 10.1007/s11120-020-00792-1. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Photosynth Res. 2021. PMID: 33146872
-
In silico screening for candidate chassis strains of free fatty acid-producing cyanobacteria.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 5;18(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3389-4. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28056772 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic analysis of parallel-evolved cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 under acid stress.Photosynth Res. 2015 Aug;125(1-2):243-54. doi: 10.1007/s11120-015-0111-3. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Photosynth Res. 2015. PMID: 25736465
-
Current knowledge and recent advances in understanding metabolism of the model cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803.Biosci Rep. 2020 Apr 30;40(4):BSR20193325. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193325. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32149336 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Addinall, S. G., and B. Holland. 2002. The tubulin ancestor, FtsZ, draughtsman, designer and driving force for bacterial cytokinesis. J. Mol. Biol. 318:219-236. - PubMed
-
- den Blaauwen, T., M. A. de Pedro, M. Nguyen-Disteche, and J. A. Ayala. 2008. Morphogenesis of rod-shaped sacculi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 32:321-344. - PubMed
-
- Di Lallo, G., M. Fagioli, D. Barionovi, P. Ghelardini, and L. Paolozzi. 2003. Use of a two-hybrid assay to study the assembly of a complex multicomponent protein machinery: bacterial septosome differentiation. Microbiology 149:3353-3359. - PubMed
-
- Domain, F., L. Houot, F. Chauvat, and C. Cassier-Chauvat. 2004. Function and regulation of the cyanobacterial genes lexA, recA and ruvB: LexA is critical to the survival of cells facing inorganic carbon starvation. Mol. Microbiol. 53:65-80. - PubMed
-
- Ebersbach, G., E. Galli, J. Moller-Jensen, J. Lowe, and K. Gerdes. 2008. Novel coiled-coil cell division factor ZapB stimulates Z ring assembly and cell division. Mol. Microbiol. 68:720-735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

