The rice aquaporin Lsi1 mediates uptake of methylated arsenic species
- PMID: 19542298
- PMCID: PMC2719116
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.140350
The rice aquaporin Lsi1 mediates uptake of methylated arsenic species
Abstract
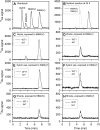
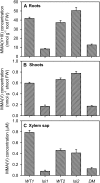
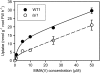
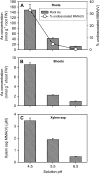
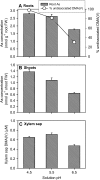
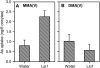
Pentavalent methylated arsenic (As) species such as monomethylarsonic acid [MMA(V)] and dimethylarsinic acid [DMA(V)] are used as herbicides or pesticides, and can also be synthesized by soil microorganisms or algae through As methylation. The mechanism of MMA(V) and DMA(V) uptake remains unknown. Recent studies have shown that arsenite is taken up by rice (Oryza sativa) roots through two silicon transporters, Lsi1 (the aquaporin NIP2;1) and Lsi2 (an efflux carrier). Here we investigated whether these two transporters also mediate the uptake of MMA(V) and DMA(V). MMA(V) was partly reduced to trivalent MMA(III) in rice roots, but only MMA(V) was translocated to shoots. DMA(V) was stable in plants. The rice lsi1 mutant lost about 80% and 50% of the uptake capacity for MMA(V) and DMA(V), respectively, compared with the wild-type rice, whereas Lsi2 mutation had little effect. The short-term uptake kinetics of MMA(V) can be described by a Michaelis-Menten plus linear model, with the wild type having 3.5-fold higher V(max) than the lsi1 mutant. The uptake kinetics of DMA(V) were linear with the slope being 2.8-fold higher in the wild type than the lsi1 mutant. Heterologous expression of Lsi1 in Xenopus laevis oocytes significantly increased the uptake of MMA(V) but not DMA(V), possibly because of a very limited uptake of the latter. Uptake of MMA(V) and DMA(V) by wild-type rice was increased as the pH of the medium decreased, consistent with an increasing proportion of the undissociated species. The results demonstrate that Lsi1 mediates the uptake of undissociated methylated As in rice roots.
Figures


References
-
- Abbas MHH, Meharg AA (2008) Arsenate, arsenite and dimethyl arsinic acid (DMA) uptake and tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Soil 304 277–289
-
- Aposhian HV, Zakharyan RA, Avram MD, Sampayo-Reyes A, Wollenberg ML (2004) A review of the enzymology of arsenic metabolism and a new potential role of hydrogen peroxide in the detoxication of the trivalent arsenic species. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 198 327–335 - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee H, Rosen BP (2007) Arsenic metabolism in prokaryotic and eukaryotic microbes. In DH Nies, S Silver, eds, Molecular Microbiology of Heavy Metals, Vol Microbiol Monograph 6. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 371–406
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

