Major role of gamma delta T cells in the generation of IL-17+ uveitogenic T cells
- PMID: 19542467
- PMCID: PMC4077214
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900241
Major role of gamma delta T cells in the generation of IL-17+ uveitogenic T cells
Abstract
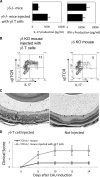
We show that in vitro activation of interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP)-specific T cells from C57BL/6 mice immunized with an uveitogenic IRBP peptide (IRBP(1-20)) under TH17-polarizing conditions is associated with increased expansion of T cells expressing the gammadelta TCR. We also show that highly purified alphabeta or gammadelta T cells from C57BL/6 mice immunized with IRBP(1-20) produced only small amounts of IL-17 after exposure to the immunizing Ag in vitro, whereas a mixture of the same T cells produced greatly increased amounts of IL-17. IRBP-induced T cells from IRBP-immunized TCR-delta(-/-) mice on the C57BL/6 genetic background produced significantly lower amounts of IL-17 than did wild-type C57BL/6 mice and had significantly decreased experimental autoimmune uveitis-inducing ability. However, reconstitution of the TCR-delta(-/-) mice before immunization with a small number of gammadelta T cells from IRBP-immunized C57BL/6 mice restored the disease-inducing capability of their IRBP-specific T cells and greatly enhanced the generation of IL-17(+) T cells in the recipient mice. Our study suggests that gammadelta T cells are important in the generation and activation of IL-17-producing autoreactive T cells and play a major role in the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune uveitis.
Figures




References
-
- Faure JP. Autoimmunity and the retina. Curr. Top. Eye Res. 1980;2:215–302. - PubMed
-
- Wacker WB, Donoso LA, Kalsow CM, Yankeelov JA, Jr., Organisciak DT. Experimental allergic uveitis: isolation, characterization, and localization of a soluble uveitopathogenic antigen from bovine retina. J. Immunol. 1977;119:1949–1958. - PubMed
-
- Caspi RR, Roberge FG, McAllister CG, El-Saied M, Kuwabara T, Gery I, Hanna E, Nussenblatt RB. T cell lines mediating experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in the rat. J. Immunol. 1986;136:928–933. - PubMed
-
- Fox GM, Redmond TM, Wiggert B, Kuwabara T, Chader GJ, Gery I. Dissociation between lymphocyte activation for proliferation and for the capacity to adoptively transfer uveoretinitis. J. Immunol. 1987;138:3242–3246. - PubMed
-
- Shao H, Liao T, Ke Y, Shi H, Kaplan HJ, Sun D. Severe chronic experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) of the C57BL/6 mouse induced by adoptive transfer of IRBP1–20-specific T cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2006;82:323–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

