The role of nuclear pores in gene regulation, development and disease
- PMID: 19543230
- PMCID: PMC2727434
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.147
The role of nuclear pores in gene regulation, development and disease
Erratum in
- EMBO Rep. 2009 Aug;10(8):934
Abstract
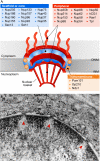
Nuclear-pore complexes (NPCs) are large protein channels that span the nuclear envelope (NE), which is a double membrane that encloses the nuclear genome of eukaryotes. Each of the typically 2,000-4,000 pores in the NE of vertebrate cells is composed of multiple copies of 30 different proteins known as nucleoporins. The evolutionarily conserved NPC proteins have the well-characterized function of mediating the transport of molecules between the nucleoplasm and the cytoplasm. Mutations in nucleoporins are often linked to specific developmental defects and disease, and the resulting phenotypes are usually interpreted as the consequences of perturbed nuclear transport activity. However, recent evidence suggests that NPCs have additional functions in chromatin organization and gene regulation, some of which might be independent of nuclear transport. Here, we review the transport-dependent and transport-independent roles of NPCs in the regulation of nuclear function and gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar A, Gasser SM (2007) The nuclear envelope and transcriptional control. Nat Rev Genet 8: 507–517 - PubMed
-
- Alber F et al. (2007) The molecular architecture of the nuclear pore complex. Nature 450: 695–701 - PubMed
-
- Ball JR, Dimaano C, Bilak A, Kurchan E, Zundel MT, Ullman KS (2007) Sequence preference in RNA recognition by the nucleoporin Nup153. J Biol Chem 282: 8734–8740 - PubMed
-
- Basel-Vanagaite L et al. (2006) Mutated nup62 causes autosomal recessive infantile bilateral striatal necrosis. Ann Neurol 60: 214–222 - PubMed
-
- Beck M, Lucic V, Forster F, Baumeister W, Medalia O (2007) Snapshots of nuclear pore complexes in action captured by cryo-electron tomography. Nature 449: 611–615 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

