Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury through upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in adult guinea pigs
- PMID: 19543301
- PMCID: PMC4085733
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.57
Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury through upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in adult guinea pigs
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the protection and the anti-oxidative mechanism afforded by chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia (CIHH) against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in guinea pig hearts.
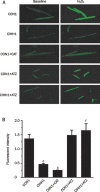
Methods: Adult male guinea pigs were exposed to CIHH by mimicking a 5000 m high altitude (p(B)=404 mmHg, p(O2)=84 mmHg) in a hypobaric chamber for 6 h/day for 28 days. Langendorff-perfused isolated guinea pig hearts were used to measure variables of left ventricular function during baseline perfusion, ischemia and the reperfusion period. The activity and protein expression of antioxidant enzymes in the left myocardium were evaluated using biochemical methods and Western blotting, respectively. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) were assessed using ROS-sensitive fluorescence.
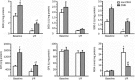
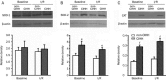
Results: After 30 min of global no-flow ischemia followed by 60 min of reperfusion, myocardial function had better recovery rates in CIHH guinea pig hearts than in control hearts. The activity and protein expression of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) were significantly increased in the myocardium of CIHH guinea pigs. Pretreatment of control hearts with an antioxidant mixture containing SOD and CAT exerted cardioprotective effects similar to CIHH. The irreversible CAT inhibitor aminotriazole (ATZ) abolished the cardioprotection of CIHH. Cardiac contractile dysfunction and oxidative stress induced by exogenous hydrogen peroxide (H(2)O(2)) were attenuated by CIHH and CAT.
Conclusions: These data suggest that CIHH protects the heart against I/R injury through upregulation of antioxidant enzymes in guinea pig.Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2009) 30: 947-955; doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.57; published online 22 June 2009.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Protective effect of intermittent hypobaric hypoxia on cardiomyocytes injury induced by hydrogen peroxide].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012 May;28(3):199-202. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22860413 Chinese.
-
Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia prevents cardiac dysfunction through enhancing antioxidation in fructose-fed rats.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 May;91(5):332-7. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2012-0059. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23656204
-
Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced calcium overload in heart via Na/Ca2+ exchanger in developing rats.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(2):313-24. doi: 10.1159/000363001. Epub 2014 Jul 8. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25096990
-
Beneficial effects of intermittent hypobaric hypoxia on the body.Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Nov;28(6):504-9. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23581179 Review.
-
Status of myocardial antioxidants in ischemia-reperfusion injury.Cardiovasc Res. 2000 Aug 18;47(3):446-56. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00078-x. Cardiovasc Res. 2000. PMID: 10963718 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased SIRT3 in aged human mesenchymal stromal/stem cells increases cellular susceptibility to oxidative stress.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Nov;18(11):2298-310. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12395. Epub 2014 Sep 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 25210848 Free PMC article.
-
[The Effect of Short-Term Intermittent Hypoxia Exposure on Mouse Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Cardiac Function].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Jan;53(1):98-104. doi: 10.12182/20220160103. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 35048607 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Ω3 Supplementation and intermittent hypobaric hypoxia induce cardioprotection enhancing antioxidant mechanisms in adult rats.Mar Drugs. 2015 Feb 4;13(2):838-60. doi: 10.3390/md13020838. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25658050 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term exercise provides left ventricular myocardial protection against intermittent hypoxia-induced apoptosis in rats.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011 Aug;111(8):1939-50. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1824-9. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21249391
-
The effect of chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia improving liver damage in metabolic syndrome rats through ferritinophagy.Pflugers Arch. 2023 Nov;475(11):1251-1263. doi: 10.1007/s00424-023-02860-6. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Pflugers Arch. 2023. PMID: 37747537
References
-
- Zhuang J, Zhou ZN. Protective effects of intermittent hypoxic adaptation on myocardium and its mechanism. Biol Signals Recept. 1999;8:316–22. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Yang HT, Zhou ZN. Cardioprotection of intermittent hypoxia. Acta Physiol Sin. 2007;59:601–13. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Zhong N, Zhou ZN. Effects of intermittent hypoxia on action potential and contraction in non-ischemic and ischemic rat papillary muscle. Life Sci. 2000;67:2465–71. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Zhong N, Zhu HF, Zhou ZN. Antiarrhythmic and antioxidative effects of intermittent hypoxia exposure on rat myocardium. Acta Physiol Sin. 2000;52:89–92. - PubMed
-
- Zong P, Setty S, Sun W, Martinez R, Tune JD, Ehrenburg IV, et al. Intermittent hypoxic training protects canine myocardium from infarction. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2004;229:806–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

