A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 19543373
- PMCID: PMC2689936
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000529
A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies
Abstract
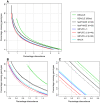
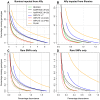
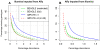
Genotype imputation methods are now being widely used in the analysis of genome-wide association studies. Most imputation analyses to date have used the HapMap as a reference dataset, but new reference panels (such as controls genotyped on multiple SNP chips and densely typed samples from the 1,000 Genomes Project) will soon allow a broader range of SNPs to be imputed with higher accuracy, thereby increasing power. We describe a genotype imputation method (IMPUTE version 2) that is designed to address the challenges presented by these new datasets. The main innovation of our approach is a flexible modelling framework that increases accuracy and combines information across multiple reference panels while remaining computationally feasible. We find that IMPUTE v2 attains higher accuracy than other methods when the HapMap provides the sole reference panel, but that the size of the panel constrains the improvements that can be made. We also find that imputation accuracy can be greatly enhanced by expanding the reference panel to contain thousands of chromosomes and that IMPUTE v2 outperforms other methods in this setting at both rare and common SNPs, with overall error rates that are 15%-20% lower than those of the closest competing method. One particularly challenging aspect of next-generation association studies is to integrate information across multiple reference panels genotyped on different sets of SNPs; we show that our approach to this problem has practical advantages over other suggested solutions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Gudmundsson J, Sulem P, Manolescu A, Amundadottir LT, Gudbjartsson D, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a second prostate cancer susceptibility variant at 8q24. Nat Genet. 2007;39:631–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

