Connecting quorum sensing, c-di-GMP, pel polysaccharide, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through tyrosine phosphatase TpbA (PA3885)
- PMID: 19543378
- PMCID: PMC2691606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000483
Connecting quorum sensing, c-di-GMP, pel polysaccharide, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through tyrosine phosphatase TpbA (PA3885)
Abstract
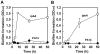
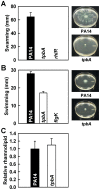
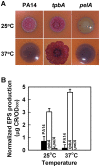
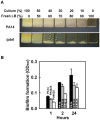
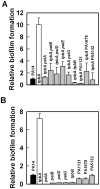
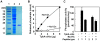
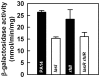
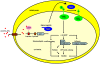
With the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, quorum sensing based on homoserine lactones was found to influence biofilm formation. Here we discern a mechanism by which quorum sensing controls biofilm formation by screening 5850 transposon mutants of P. aeruginosa PA14 for altered biofilm formation. This screen identified the PA3885 mutant, which had 147-fold more biofilm than the wild-type strain. Loss of PA3885 decreased swimming, abolished swarming, and increased attachment, although this did not affect production of rhamnolipids. The PA3885 mutant also had a wrinkly colony phenotype, formed pronounced pellicles, had substantially more aggregation, and had 28-fold more exopolysaccharide production. Expression of PA3885 in trans reduced biofilm formation and abolished aggregation. Whole transcriptome analysis showed that loss of PA3885 activated expression of the pel locus, an operon that encodes for the synthesis of extracellular matrix polysaccharide. Genetic screening identified that loss of PelABDEG and the PA1120 protein (which contains a GGDEF-motif) suppressed the phenotypes of the PA3885 mutant, suggesting that the function of the PA3885 protein is to regulate 3,5-cyclic diguanylic acid (c-di-GMP) concentrations as a phosphatase since c-di-GMP enhances biofilm formation by activating PelD, and c-di-GMP inhibits swarming. Loss of PA3885 protein increased cellular c-di-GMP concentrations; hence, PA3885 protein is a negative regulator of c-di-GMP production. Purified PA3885 protein has phosphatase activity against phosphotyrosine peptides and is translocated to the periplasm. Las-mediated quorum sensing positively regulates expression of the PA3885 gene. These results show that the PA3885 protein responds to AHL signals and likely dephosphorylates PA1120, which leads to reduced c-di-GMP production. This inhibits matrix exopolysaccharide formation, which leads to reduced biofilm formation; hence, we provide a mechanism for quorum sensing control of biofilm formation through the pel locus and suggest PA3885 should be named TpbA for tyrosine phosphatase related to biofilm formation and PA1120 should be TpbB.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduced Intracellular c-di-GMP Content Increases Expression of Quorum Sensing-Regulated Genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Oct 17;7:451. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00451. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29090193 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Biochemical Analysis of Tyrosine Phosphatase Related to Biofilm Formation A (TpbA) from the Opportunistic Pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0124330. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124330. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909591 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity in surface sensing suggests a division of labor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa populations.Elife. 2019 Jun 10;8:e45084. doi: 10.7554/eLife.45084. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31180327 Free PMC article.
-
c-di-GMP and its Effects on Biofilm Formation and Dispersion: a Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Review.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Apr;3(2):MB-0003-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0003-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26104694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas and Burkholderia species.Environ Microbiol. 2014 Jul;16(7):1961-81. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12448. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24592823 Review.
Cited by
-
Type 3 Fimbriae Encoded on Plasmids Are Expressed from a Unique Promoter without Affecting Host Motility, Facilitating an Exceptional Phenotype That Enhances Conjugal Plasmid Transfer.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 14;11(9):e0162390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162390. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27627107 Free PMC article.
-
The Sia System and c-di-GMP Play a Crucial Role in Controlling Cell-Association of Psl in Planktonic P. aeruginosa.J Bacteriol. 2022 Dec 20;204(12):e0033522. doi: 10.1128/jb.00335-22. Epub 2022 Nov 30. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 36448788 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Biological and Computational Methods for Designing Mechanism-Informed Anti-biofilm Agents.Front Microbiol. 2021 Apr 13;12:640787. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.640787. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33927701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type IV pilus assembly in Pseudomonas aeruginosa over a broad range of cyclic di-GMP concentrations.J Bacteriol. 2012 Aug;194(16):4285-94. doi: 10.1128/JB.00803-12. Epub 2012 Jun 8. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22685276 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the regulatory mechanism of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa YfiBNR system.Protein Cell. 2016 Jun;7(6):403-16. doi: 10.1007/s13238-016-0264-7. Epub 2016 Apr 25. Protein Cell. 2016. PMID: 27113583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman L, Kolter R. Genes involved in matrix formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 biofilms. Mol Microbiol. 2004;51:675–690. - PubMed
-
- Ross P, Mayer R, Weinhouse H, Amikam D, Huggirat Y, et al. The cyclic diguanylic acid regulatory system of cellulose synthesis in Acetobacter xylinum. Chemical synthesis and biological activity of cyclic nucleotide dimer, trimer, and phosphothioate derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:18933–18943. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

