Epigenetic silencing of host cell defense genes enhances intracellular survival of the rickettsial pathogen Anaplasma phagocytophilum
- PMID: 19543390
- PMCID: PMC2694362
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000488
Epigenetic silencing of host cell defense genes enhances intracellular survival of the rickettsial pathogen Anaplasma phagocytophilum
Abstract
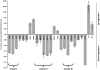
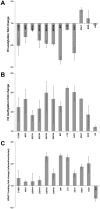
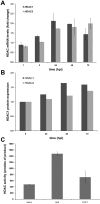
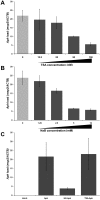
Intracellular bacteria have evolved mechanisms that promote survival within hostile host environments, often resulting in functional dysregulation and disease. Using the Anaplasma phagocytophilum-infected granulocyte model, we establish a link between host chromatin modifications, defense gene transcription and intracellular bacterial infection. Infection of THP-1 cells with A. phagocytophilum led to silencing of host defense gene expression. Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) expression, activity and binding to the defense gene promoters significantly increased during infection, which resulted in decreased histone H3 acetylation in infected cells. HDAC1 overexpression enhanced infection, whereas pharmacologic and siRNA HDAC1 inhibition significantly decreased bacterial load. HDAC2 does not seem to be involved, since HDAC2 silencing by siRNA had no effect on A. phagocytophilum intracellular propagation. These data indicate that HDAC up-regulation and epigenetic silencing of host cell defense genes is required for A. phagocytophilum infection. Bacterial epigenetic regulation of host cell gene transcription could be a general mechanism that enhances intracellular pathogen survival while altering cell function and promoting disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic regulation of defense genes by histone deacetylase1 in human cell line-derived macrophages promotes intracellular survival of Leishmania donovani.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Apr 10;14(4):e0008167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008167. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32275661 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of Host Cell Surface Protein Disulfide Isomerase by Anaplasma phagocytophilum Asp14 Enables Pathogen Infection.mBio. 2020 Jan 28;11(1):e03141-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03141-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 31992623 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from Anaplasma phagocytophilum: chromatin remodeling by bacterial effectors.Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2012 Oct;12(5):380-7. doi: 10.2174/187152612804142242. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2012. PMID: 23082961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum increases cathepsin L activity, thereby globally influencing neutrophil function.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):4905-12. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00851-08. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18765732 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking in and grabbing a meal: Anaplasma phagocytophilum cellular invasion, nutrient acquisition, and promising tools for their study.Microbes Infect. 2013 Dec;15(14-15):1017-25. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Microbes Infect. 2013. PMID: 24141091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of Anaplasma phagocytophilum during infection of human myeloid cells identifies a protein that is pronouncedly upregulated on the infectious dense-cored cell.Infect Immun. 2011 Nov;79(11):4696-707. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05658-11. Epub 2011 Aug 15. Infect Immun. 2011. PMID: 21844238 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity in rickettsial infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 May 9;13:1187267. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1187267. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37228668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T Lymphocyte Interferon-gamma Response to Anaplasmataceae-related Major Surface Proteins and Ankyrin A in Fibromyalgia.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(11):1392-1399. doi: 10.2174/0118715273274091231207101522. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38375844
-
Epigenetic reprogramming of host genes in viral and microbial pathogenesis.Trends Microbiol. 2010 Oct;18(10):439-47. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.07.003. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20724161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC3 Regulates Gingival Fibroblast Inflammatory Responses in Periodontitis.J Dent Res. 2020 Jan;99(1):98-106. doi: 10.1177/0022034519885088. Epub 2019 Nov 6. J Dent Res. 2020. PMID: 31693860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galan JE, Cossart P. Host-pathogen interactions: a diversity of themes, a variety of molecular machines. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2005;8:1–3. - PubMed
-
- Bryant PA, Venter D, Robins-Browne R, Curtis N. Chips with everything: DNA microarrays in infectious diseases. Lancet Infectious Diseases. 2004;4:100–111. - PubMed
-
- Glaser KB, Staver MJ, Waring JF, Stender J, Ulrich RG, et al. Gene expression profiling of multiple histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors: defining a common gene set produced by HDAC inhibition in T24 and MDA carcinoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003;2:151–163. - PubMed
-
- Lee HS, Park MH, Yang SJ, Jung HY, Byun SS, et al. Gene expression analysis in human gastric cancer cell line treated with trichostatin A and S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine using cDNA microarray. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004;27:1497–1503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

