The role of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors in prostate pathophysiology: Is there an additional advantage to inhibition of type 1 isoenzyme?
- PMID: 19543428
- PMCID: PMC2698784
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.1114
The role of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors in prostate pathophysiology: Is there an additional advantage to inhibition of type 1 isoenzyme?
Abstract
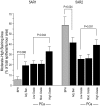
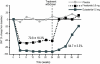
Normal growth and function of the prostate are contingent on the reduction of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by 5-alpha reductase (5-AR) enzymes types 1 and 2. It has been theorized that an overabundance of DHT may be implicated in the pathogenesis of both benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. Inhibitors of 5-AR such as dutasteride and finasteride may therefore have an important role in the prevention and treatment of BPH and prostate cancer. Dutasteride provides greater suppression of DHT than finasteride, thereby underlying the hypothesis that inhibition of both type 1 and type 2 would provide correspondingly greater protection than inhibition of type 2 alone. We review the potential significance of the 5-AR inhibitors in reducing the risk of prostate cancer according to the basic biology of prostate disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia.World J Urol. 2002 Apr;19(6):413-25. doi: 10.1007/s00345-002-0248-5. World J Urol. 2002. PMID: 12022710 Review.
-
Dihydrotestosterone and the concept of 5alpha-reductase inhibition in human benign prostatic hyperplasia.Eur Urol. 2000 Apr;37(4):367-80. doi: 10.1159/000020181. Eur Urol. 2000. PMID: 10765065 Review.
-
[Dihydrotestosterone and the role of 5 alpha-reductase inhibitors in benign prostatic hyperplasia].Urologe A. 2002 Sep;41(5):412-24. doi: 10.1007/s00120-002-0230-2. Urologe A. 2002. PMID: 12426858 Review. German.
-
Marked suppression of dihydrotestosterone in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia by dutasteride, a dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 May;89(5):2179-84. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030330. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15126539 Clinical Trial.
-
Differential effect of finasteride on the tissue androgen concentrations in benign prostatic hyperplasia.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1997 Feb;46(2):137-44. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2265.1997.950908.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1997. PMID: 9135694 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Potential of Phytochemicals from Prunus africana (Hook f.) Kalkman Stem Bark for Chemoprevention and Chemotherapy of Prostate Cancer.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:3014019. doi: 10.1155/2017/3014019. Epub 2017 Feb 13. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28286531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Attenuates the Proliferation of Prostatic Stromal Cells in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia by Regulating Cell Cycle Progression, Apoptosis, Signaling Pathways, BPH Markers, and NF- κB Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 31;22(11):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115969. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34073143 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine ameliorates testosterone-induced benign prostate hyperplasia in rats.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Dec 20;21(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03472-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34930229 Free PMC article.
-
Use of 5α-reductase inhibitor and delay in prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment.Int Braz J Urol. 2020 May-Jun;46(3):456-458. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2020.03.02. Int Braz J Urol. 2020. PMID: 32167713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ixeris polycephala Extract Alleviates Progression of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia via Modification of Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Inflammation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;17(8):1032. doi: 10.3390/ph17081032. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruchovsky N, Wilson JD. The conversion of testosterone to 5-alpha-androstan-17-beta-ol-3-one by rat prostate in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1968;243:2012–21. - PubMed
-
- Bruchovsky N, Wilson JD. The intranuclear binding of testosterone and 5-alpha-androstan-17-beta-ol-3-one by rat prostate. J Biol Chem. 1968;243:5953–60. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KM, Liao S. Selective retention of dihydrotestosterone by prostatic nuclei. Nature. 1968;219:277–9. - PubMed
-
- Imamoto T, Suzuki H, Yano M, et al. The role of testosterone in the pathogenesis of prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 2008;15:472–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
