The ATP-binding cassette family: a structural perspective
- PMID: 19544044
- PMCID: PMC11115812
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0064-9
The ATP-binding cassette family: a structural perspective
Abstract
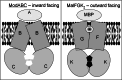
The ATP-binding cassette family is one of the largest groupings of membrane proteins, moving allocrites across lipid membranes, using energy from ATP. In bacteria, they reside in the inner membrane and are involved in both uptake and export. In eukaryotes, these transporters reside in the cell's internal membranes as well as in the plasma membrane and are unidirectional-out of the cytoplasm. The range of substances that these proteins can transport is huge, which makes them interesting for structure-function studies. Moreover, their abundance in nature has made them targets for structural proteomics consortia. There are eight independent structures for ATP-binding cassette transporters, making this one of the best characterised membrane protein families. Our understanding of the mechanism of transport across membranes and membrane protein structure in general has been enhanced by recent developments for this family.
Figures








References
-
- Dean M, Hamon Y, Chimini G. The human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter superfamily. J Lipid Res. 2001;42:1007–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

