Regulation of boundary cap neural crest stem cell differentiation after transplantation
- PMID: 19544468
- PMCID: PMC2733376
- DOI: 10.1002/stem.77
Regulation of boundary cap neural crest stem cell differentiation after transplantation
Abstract
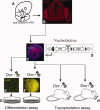
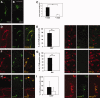
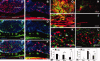
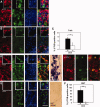
Success of cell replacement therapies for neurological disorders will depend largely on the optimization of strategies to enhance viability and control the developmental fate of stem cells after transplantation. Once transplanted, stem/progenitor cells display a tendency to maintain an undifferentiated phenotype or differentiate into inappropriate cell types. Gain and loss of function experiments have revealed key transcription factors which drive differentiation of immature stem/progenitor cells toward more mature stages and eventually to full differentiation. An attractive course of action to promote survival and direct the differentiation of transplanted stem cells to a specific cell type would therefore be to force expression of regulatory differentiation molecules in already transplanted stem cells, using inducible gene expression systems which can be controlled from the outside. Here, we explore this hypothesis by employing a tetracycline gene regulating system (Tet-On) to drive the differentiation of boundary cap neural crest stem cells (bNCSCs) toward a sensory neuron fate after transplantation. We induced the expression of the key transcription factor Runx1 in Sox10-expressing bNCSCs. Forced expression of Runx1 strongly increased transplant survival in the enriched neurotrophic environment of the dorsal root ganglion cavity, and was sufficient to guide differentiation of bNCSCs toward a nonpeptidergic nociceptive sensory neuron phenotype both in vitro and in vivo after transplantation. These findings suggest that exogenous activation of transcription factors expression after transplantation in stem/progenitor cell grafts can be a constructive approach to control their survival as well as their differentiation to the desired type of cell and that the Tet-system is a useful tool to achieve this.
Figures
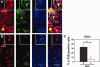
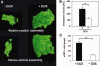
References
-
- Bithell A, Williams BP. Neural stem cells and cell replacement therapy: Making the right cells. Clin Sci (Lond) 2005;108:13–22. - PubMed
-
- Brederlau A, Correia AS, Anisimov SV, et al. Transplantation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cells to a rat model of Parkinson's disease: Effect of in vitro differentiation on graft survival and teratoma formation. Stem Cells. 2006;24:1433–1440. - PubMed
-
- Martino G, Pluchino S. The therapeutic potential of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:395–406. - PubMed
-
- Kozlova EN, Rosario CM, Stromberg I, et al. Peripherally grafted human foetal dorsal root ganglion cells extend axons into the spinal cord of adult host rats by circumventing dorsal root entry zone astrocytes. Neuroreport. 1995;6:269–272. - PubMed
-
- Kozlova EN, Seiger A, Aldskogius H. Human dorsal root ganglion neurons from embryonic donors extend axons into the host rat spinal cord along laminin-rich peripheral surroundings of the dorsal root transitional zone. J Neurocytol. 1997;26:811–822. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

