Effect of protein structure on deamidation rate in the Fc fragment of an IgG1 monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 19544580
- PMCID: PMC2776945
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.173
Effect of protein structure on deamidation rate in the Fc fragment of an IgG1 monoclonal antibody
Abstract
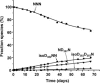
The effects of secondary structure on asparagine (N) deamidation in a 22 amino acid sequence (369-GFYPSDIAVEWESNGQPENNYK-390) of the crystallizable (Fc) fragment of a human monoclonal antibody (Fc IgG1) were investigated using high-resolution ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC/MS). Samples containing either the intact Fc IgG (approximately 50 kD) ("intact protein"), or corresponding synthetic peptides ("peptide") were stored in Tris buffer at 37 degrees C and pH 7.5 for up to forty days, then subjected to UPLC/MS analysis with high energy MS1 fragmentation. The peptide deamidated only at N(382) to form the isoaspartate (isoD(382)) and aspartate (D(382)) products in the ratio of approximately 4:1, with a half-life of approximately 3.4 days. The succinimide intermediate (Su(382)) was also detected; deamidation was not observed for the other two sites (N(387) and N(388)) in peptide samples. The intact protein showed a 30-fold slower overall deamidation half-life of approximately 108 days to produce the isoD(382) and D(387) products, together with minor amounts of D(382). Surprisingly, the D(382) and isoD(387) products were not detected in intact protein samples and, as in the peptide samples, deamidation was not detected at N(388). The results indicate that higher order structure influences both the rate of N-deamidation and the product distribution.
Figures


 ,
,  , and
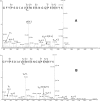
, and  ions, together with the elution and fragmentation patterns of synthetic peptide standards (see text), identifies the peaks as the IsoD382NN, NNN (parent) and D382NN forms, respectively. See the electronic version of this article for enlarged figures.
ions, together with the elution and fragmentation patterns of synthetic peptide standards (see text), identifies the peaks as the IsoD382NN, NNN (parent) and D382NN forms, respectively. See the electronic version of this article for enlarged figures.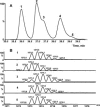


References
-
- Chowdhury PS, Wu H. Tailor-made antibody therapeutics. Methods. 2005;36:11–24. - PubMed
-
- Gottschalk U. Downstream processing of monoclonal antibodies: from high dilution to high purity. Bio Pharm Int. 2005;18:42–44. 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58.
-
- Aswad DW. Deamidation and isoaspartate formation in peptides and proteins. Ann Arbor: CRC Press; 1995. p. 259.
-
- Jenkins N, Murphy L, Tyther R. Post-translational modifications of recombinant proteins: significance for biopharmaceuticals. Mol Biotechnol. 2008;39:113–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

