Decreased expression of colonic Slc26a3 and carbonic anhydrase iv as a cause of fatal infectious diarrhea in mice
- PMID: 19546193
- PMCID: PMC2738044
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00225-09
Decreased expression of colonic Slc26a3 and carbonic anhydrase iv as a cause of fatal infectious diarrhea in mice
Abstract
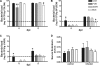
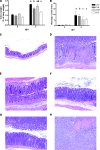
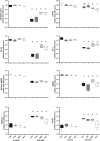
Citrobacter rodentium causes epithelial hyperplasia and colitis and is used as a model for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli infections. Little or no mortality develops in most inbred strains of mice, but C3H and FVB/N mice exhibit fatal outcomes of infection. Here we test the hypothesis that decreased intestinal transport activity during C. rodentium infection results in fatality in C3H/HeOu and FVB/N mice. Susceptible strains were compared to resistant C57BL/6 mice and to inbred strains SWR and SJL of Swiss origin, which have not been previously characterized for outcomes of C. rodentium infection. Mortality in susceptible strains C3H/HeOu and FVB/N was associated with significant fluid loss in feces, a remarkable downregulation of Slc26a3 and carbonic anhydrase IV (CAIV) message and protein expression, retention of chloride in stool, and hypochloremia, suggesting defects in intestinal chloride absorption. SWR, SJL, and C57BL/6 mice were resistant and survived the infection. Fluid therapy fully prevented mortality in C3H/HeOu and FVB/N mice without affecting clinical disease. Common pathogenic mechanisms, such as decreased levels of expression of Slc26a3 and CAIV, affect intestinal ion transport in C. rodentium-infected FVB and C3H mice, resulting in profound electrolyte loss, dehydration, and mortality. Intestinal chloride absorption pathways are likely a potential target for the treatment of infectious diarrhea.
Figures


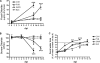
References
-
- Alleva, D. G., E. B. Johnson, J. Wilson, D. I. Beller, and P. J. Conlon. 2001. SJL and NOD macrophages are uniquely characterized by genetically programmed, elevated expression of the IL-12(p40) gene, suggesting a conserved pathway for the induction of organ-specific autoimmunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 69440-448. - PubMed
-
- Alrefai, W. A., X. Wen, W. Jiang, J. P. Katz, K. A. Steinbrecher, M. B. Cohen, I. R. Williams, P. K. Dudeja, and G. D. Wu. 2007. Molecular cloning and promoter analysis of downregulated in adenoma (DRA). Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 293G923-G934. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, B. V., F. B. Loiselle, C. T. Supuran, G. J. Schwartz, and J. R. Casey. 2003. Direct extracellular interaction between carbonic anhydrase IV and the human NBC1 sodium/bicarbonate co-transporter. Biochemistry 4212321-12329. - PubMed
-
- Baqar, S., E. Burg, and J. R. Murphy. 2000. Mouse models of Campylobacter jejuni infection, p. 223-240. In O. Zak and M. A. Sande (ed.), Handbook of animal models of infection. Experimental models in antimicrobial chemotherapy. Academic Press, San Diego, CA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

