Effect of Candida glabrata FKS1 and FKS2 mutations on echinocandin sensitivity and kinetics of 1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase: implication for the existing susceptibility breakpoint
- PMID: 19546367
- PMCID: PMC2737881
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00443-09
Effect of Candida glabrata FKS1 and FKS2 mutations on echinocandin sensitivity and kinetics of 1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase: implication for the existing susceptibility breakpoint
Abstract
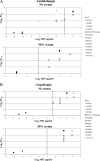
Thirteen Candida glabrata strains harboring a range of mutations in hot spot regions of FKS1 and FKS2 were studied. The mutations were linked to an echinocandin reduced susceptibility phenotype. Sequence alignments showed that 11 out of the 13 mutants harbored a mutation in FKS1 or FKS2 not previously implicated in echinocandin reduced susceptibility in C. glabrata. A detailed kinetic characterization demonstrated that amino acid substitutions in Fks1p and Fks2p reduced drug sensitivity in mutant 1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase by 2 to 3 log orders relative to that in wild-type enzyme. These mutations were also found to reduce the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme (Vmax) and to influence the relative expression of FKS genes. In view of the association of FKS mutations and reduced susceptibility of 1,3-beta-D-glucan synthase, an evaluation of the new CLSI echinocandin susceptibility breakpoint was conducted. Only 3 of 13 resistant fks mutants (23%) were considered anidulafungin or micafungin nonsusceptible (MIC > 2 microg/ml) by this criterion. In contrast, most fks mutants (92%) exceeded a MIC of >2 microg/ml with caspofungin. However, when MIC determinations were performed in the presence of 50% serum, all C. glabrata fks mutants showed MICs of > or = 2 microg/ml for the three echinocandin drugs. As has been observed with Candida albicans, the kinetic inhibition parameter 50% inhibitory concentration may be a better predictor of FKS-mediated resistance. Finally, the close association between FKS1/FKS2 hot spot mutations provides a basis for understanding echinocandin resistance in C. glabrata.
Figures




References
-
- Amrani, N., M. S. Sachs, and A. Jacobson. 2006. Early nonsense: mRNA decay solves a translational problem. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:415-425. - PubMed
-
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. 2008. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts. Approved standard M27-A3, 3rd ed. Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
-
- Correia, A., P. Sampaio, S. James, and C. Pais. 2006. Candida bracarensis sp. nov., a novel anamorphic yeast species phenotypically similar to Candida glabrata. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 56:313-317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

