Medication diaries do not improve outcomes with highly active antiretroviral therapy in Kenyan children: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 19549342
- PMCID: PMC2708138
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-2652-12-8
Medication diaries do not improve outcomes with highly active antiretroviral therapy in Kenyan children: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: As highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) becomes increasingly available to African children, it is important to evaluate simple and feasible methods of improving adherence in order to maximize benefits of therapy.
Methods: HIV-1-infected children initiating World Health Organization non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase-inhibitor-containing first-line HAART regimens were randomized to use medication diaries plus counselling, or counselling only (the control arm of the study). The diaries were completed daily by caregivers of children randomized to the diary and counselling arm for nine months. HIV-1 RNA, CD4+ T cell count, and z-scores for weight-for-age, height-for-age and weight-for-height were measured at a baseline and every three to six months. Self-reported adherence was assessed by questionnaires for nine months.
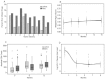
Results: Ninety HIV-1-infected children initiated HAART, and were followed for a median of 15 months (interquartile range: 2-21). Mean CD4 percentage was 17.2% in the diary arm versus 16.3% in the control arm at six months (p = 0.92), and 17.6% versus 18.9% at 15 months (p = 0.36). Virologic response with HIV-1 RNA of <100 copies/ml at nine months was similar between the two arms (50% for the diary arm and 36% for the control, p = 0.83). The weight-for-age, height-for-age and weight-for-height at three, nine and 15 months after HAART initiation were similar between arms. A trend towards lower self-reported adherence was observed in the diary versus the control arm (85% versus 92%, p = 0.08).
Conclusion: Medication diaries did not improve clinical and virologic response to HAART over a 15-month period. Children had good adherence and clinical response without additional interventions. This suggests that paediatric HAART with conventional counselling can be a successful approach. Further studies on targeted approaches for non-adherent children will be important.
Figures
References
-
- Paterson DL, Swindells S, Mohr J, Brester M, Vergis EN, Squier C, Wagener MM, Singh N. Adherence to protease inhibitor therapy and outcomes in patients with HIV infection. Ann Intern Med. 2000;12(1):21–30. - PubMed
-
- Van Dyke RB, Lee S, Johnson GM, Wiznia A, Mohan K, Stanley K, Morse EV, Krogstad PA, Nachman S. Pediatric AIDS Clinical Trials Group Adherence Subcommittee Pediatric AIDS Clinical Trials Group 377 Study Team. Reported adherence as a determinant of response to highly active antiretroviral therapy in children who have human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatrics. 2002;12(4):e6. doi: 10.1542/peds.109.4.e61. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Antiretroviral therapy of HIV infection in infants and children in resource-limited settings: towards universal access. Recommendations for a public health approach. 2006. - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency. Opinions for use of medicines outside the European Union. Aluvia H-C-764, European Public Assessment Report. 2008. http://www.emea.europa.eu/htms/human/non_eu_epar/epar/aluvia/aluvia.htm
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials