Opposing effects of SWI/SNF and Mi-2/NuRD chromatin remodeling complexes on epigenetic reprogramming by EBF and Pax5
- PMID: 19549820
- PMCID: PMC2708696
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0809485106
Opposing effects of SWI/SNF and Mi-2/NuRD chromatin remodeling complexes on epigenetic reprogramming by EBF and Pax5
Abstract
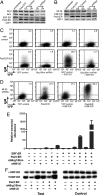
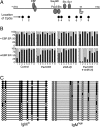
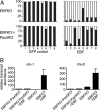
Transcriptionally silent genes are maintained in inaccessible chromatin. Accessibility of these genes requires their modification by chromatin remodeling complexes (CRCs), which are recruited to promoters by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. Early B-cell factor (EBF), which is crucial for B-cell lineage specification, reprograms mb-1 (Ig-alpha) promoters by increasing chromatin accessibility and initiating the loss of DNA methylation. In turn, this facilitates promoter activation by Pax5. Here, we investigated the roles of ATP-dependent CRCs in these mechanisms. Fusion of EBF and Pax5 with the ligand-binding domain of ERalpha allowed for 4-hydroxytamoxifen-dependent, synergistic activation of mb-1 transcription in plasmacytoma cells. Knock-down of the SWI/SNF ATPases Brg1 and Brm inhibited transcriptional activation by EBF:ER and Pax5:ER. In contrast, knock-down of the Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit Mi-2beta greatly enhanced chromatin accessibility and mb-1 transcription in response to the activators. The reduction of Mi-2beta also propagated DNA demethylation in response to EBF:ER and Pax5:ER, resulting in fully unmethylated mb-1 promoters. In EBF- or EBF/Pax5-deficient fetal liver cells, both EBF and Pax5 were required for efficient demethylation of mb-1 promoters. Together, our data suggest that Mi-2/NuRD is important for the maintenance of hypermethylated chromatin in B cells. We conclude that SWI/SNF and Mi-2/NuRD function in opposition to enable or limit the reprogramming of genes by EBF and Pax5 during B-cell development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MBD2 and multiple domains of CHD4 are required for transcriptional repression by Mi-2/NuRD complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Dec;32(24):5078-88. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00819-12. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23071088 Free PMC article.
-
DOC1-Dependent Recruitment of NURD Reveals Antagonism with SWI/SNF during Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Oral Cancer Cells.Cell Rep. 2017 Jul 5;20(1):61-75. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.020. Cell Rep. 2017. PMID: 28683324
-
Early B cell factor cooperates with Runx1 and mediates epigenetic changes associated with mb-1 transcription.Nat Immunol. 2004 Oct;5(10):1069-77. doi: 10.1038/ni1119. Epub 2004 Sep 12. Nat Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15361869
-
Dangerous liaisons: interplay between SWI/SNF, NuRD, and Polycomb in chromatin regulation and cancer.Genes Dev. 2019 Aug 1;33(15-16):936-959. doi: 10.1101/gad.326066.119. Epub 2019 May 23. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 31123059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Mi-2 related ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers.Epigenetics. 2009 May 16;4(4):209-11. doi: 10.4161/epi.8933. Epub 2009 May 6. Epigenetics. 2009. PMID: 19535903 Review.
Cited by
-
The chromatin-remodeling enzymes BRG1 and CHD4 antagonistically regulate vascular Wnt signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;32(7):1312-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06222-11. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22290435 Free PMC article.
-
EBF2 transcriptionally regulates brown adipogenesis via the histone reader DPF3 and the BAF chromatin remodeling complex.Genes Dev. 2017 Apr 1;31(7):660-673. doi: 10.1101/gad.294405.116. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28428261 Free PMC article.
-
ZNF423 and ZNF521: EBF1 Antagonists of Potential Relevance in B-Lymphoid Malignancies.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:165238. doi: 10.1155/2015/165238. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26788497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between cofactors and transcription factors in hematopoiesis and hematological malignancies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jan 20;6(1):24. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00422-1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33468999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATP dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes in embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010 Mar;6(1):62-73. doi: 10.1007/s12015-010-9120-y. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010. PMID: 20148317 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nutt SL, Kee BL. The transcriptional regulation of B-cell lineage commitment. Immunity. 2007;26:715–725. - PubMed
-
- Medina KL, et al. Defining a regulatory network for specification of the B-cell fate. Dev Cell. 2004;7:607–617. - PubMed
-
- Lin H, Grosschedl R. Failure of B-cell differentiation in mice lacking the transcription factor EBF. Nature. 1995;376:263–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

