An engineered substance P variant for receptor-mediated delivery of synthetic antibodies into tumor cells
- PMID: 19549879
- PMCID: PMC2708752
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0904907106
An engineered substance P variant for receptor-mediated delivery of synthetic antibodies into tumor cells
Abstract
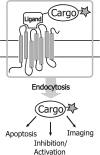
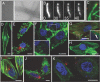
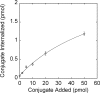
We have developed and tested a robust delivery method for the transport of proteins to the cytoplasm of mammalian cells without compromising the integrity of the cell membrane. This receptor-mediated delivery (RMD) technology utilizes a variant of substance P (SP), a neuropeptide that is rapidly internalized upon interaction with the neurokinin-1 receptor (NK1R). Cargos in the form of synthetic antibody fragments (sABs) were conjugated to the engineered SP variant (SPv) and efficiently internalized by NK1R-expressing cells. The sABs used here were generated to bind specific conformational forms of actin. The internalized proteins appear to escape the endosome and retain their binding activity within the cells as demonstrated by co-localization with the actin cytoskeleton. Further, since the NK1R is over-expressed in many cancers, SPv-mediated delivery provides a highly specific method for therapeutic utilization of affinity reagents targeting intracellular processes in diseased tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dalby B, et al. Advanced transfection with Lipofectamine 2000 reagent: primary neurons, siRNA, and high-throughput applications. Methods. 2004;33:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen LB, Calvin SA, Colvin KE, Wright M. FuGENE 6 Transfection Reagent: The gentle power. Methods. 2004;33:104–112. - PubMed
-
- Stewart KM, Horton KL, Kelley SO. Cell-penetrating peptides as delivery vehicles for biology and medicine. Org Biomol Chem. 2008;6:2242–2255. - PubMed
-
- Morris MC, Depollier J, Mery J, Heitz F, Divita G. A peptide carrier for the delivery of biologically active proteins into mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:1173–1176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

