Active Notch1 confers a transformed phenotype to primary human melanocytes
- PMID: 19549918
- PMCID: PMC2755513
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3767
Active Notch1 confers a transformed phenotype to primary human melanocytes
Abstract
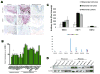
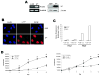
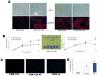
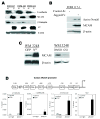
The importance of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in melanoma is underscored by the prevalence of activating mutations in N-Ras and B-Raf, yet clinical development of inhibitors of this pathway has been largely ineffective, suggesting that alternative oncogenes may also promote melanoma. Notch is an interesting candidate that has only been correlated with melanoma development and progression; a thorough assessment of tumor-initiating effects of activated Notch on human melanocytes would clarify the mounting correlative evidence and perhaps identify a novel target for an otherwise untreatable disease. Analysis of a substantial panel of cell lines and patient lesions showed that Notch activity is significantly higher in melanomas than their nontransformed counterparts. The use of a constitutively active, truncated Notch transgene construct (N(IC)) was exploited to determine if Notch activation is a "driving" event in melanocytic transformation or instead a "passenger" event associated with melanoma progression. N(IC)-infected melanocytes displayed increased proliferative capacity and biological features more reminiscent of melanoma, such as dysregulated cell adhesion and migration. Gene expression analyses supported these observations and aided in the identification of MCAM, an adhesion molecule associated with acquisition of the malignant phenotype, as a direct target of Notch transactivation. N(IC)-positive melanocytes grew at clonal density, proliferated in limiting media conditions, and also exhibited anchorage-independent growth, suggesting that Notch alone is a transforming oncogene in human melanocytes, a phenomenon not previously described for any melanoma oncogene. This new information yields valuable insight into the basic epidemiology of melanoma and launches a realm of possibilities for drug intervention in this deadly disease.
Figures

References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science (New York, NY. 1999;284:770–6. - PubMed
-
- Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC, et al. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991;66:649–61. - PubMed
-
- Shou J, Ross S, Koeppen H, de Sauvage FJ, Gao WQ. Dynamics of notch expression during murine prostate development and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7291–7. - PubMed
-
- Raafat A, Bargo S, Anver MR, Callahan R. Mammary development and tumorigenesis in mice expressing a truncated human Notch4/Int3 intracellular domain (h-Int3sh) Oncogene. 2004;23:9401–7. - PubMed
-
- Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, et al. Notch signaling induces cell cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3200–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM071695/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA117881/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA47159/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA93372/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA010815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA80999/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA098101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 AG000450/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071695/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA25874/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047159/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA098101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118871/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA025874/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA093372/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA10815/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076674/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76674/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080999/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

