Hepatitis B and long-term HIV outcomes in coinfected HAART recipients
- PMID: 19550291
- PMCID: PMC2861825
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832e463a
Hepatitis B and long-term HIV outcomes in coinfected HAART recipients
Abstract
Background: Chronic hepatitis B (CH-B) is common among HIV-infected individuals and increases liver-related mortality in the absence of HAART. The impact of CH-B on long-term HAART outcomes has not been fully characterized.
Methods: To address this question, HAART initiators enrolled in the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study were retrospectively analyzed. Patients were classified by hepatitis B category based on serology at the time of HAART initiation. The association of CH-B with mortality, AIDS-defining illnesses, CD4 cell rise, and HIV suppression was assessed using regression analysis.
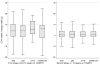
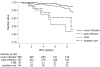
Results: Of 816 men followed for a median of 7 years on HAART, 350 were never hepatitis B virus (HBV) infected, 357 had past infection, 45 had CH-B, and 64 were only core-antibody positive. Despite HAART, AIDS-related mortality was the most common cause of death [8.3/1000 person-years (PYs)]. It was highest in those with CH-B (17/1000 PYs, 95% confidence interval 7.3, 42) and lowest among never HBV infected (2.9/1000 PYs, 95% confidence interval 1.4, 6.4). In a multivariable model, patients with CH-B had a 2.7-fold higher incidence of AIDS-related mortality compared with those never infected (P = 0.08). Non-AIDS-related mortality was also highest among those with CH-B (22/1000 PYs), primarily due to liver disease (compared to never infected, adjusted hazard ratio 4.1, P = 0.04). There was no significant difference in AIDS-defining events, HIV RNA suppression, and CD4 cell increase.
Conclusion: In HIV-infected patients receiving long-term HAART, HBV status did not influence HIV suppression or CD4 cell increase. However, mortality was highest among those with CH-B and was mostly due to liver disease despite HBV-active HAART.
2009 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: No conflicts
Figures
References
-
- Walensky RP, Paltiel AD, Losina E, Mercincavage LM, Schackman BR, Sax PE, et al. The survival benefits of AIDS treatment in the United States. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:11–19. - PubMed
-
- Lewden C, Chene G, Morlat P, Raf FF, Dupon M, Dellamonica P, et al. HIV-Infected Adults With a CD4 Cell Count Greater Than 500 Cells/mm3 on Long-Term Combination Antiretroviral Therapy Reach Same Mortality Rates as the General Population. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Lohse N, Hansen AB, Pedersen G, Kronborg G, Gerstoft J, Sorensen HT, et al. Survival of persons with and without HIV infection in Denmark, 1995–2005. Ann Intern Med. 2007;146:87–95. - PubMed
-
- de Luca A, Bugarini R, Lepri AC, Puoti M, Girardi E, Antinori A, et al. Coinfection with hepatitis viruses and outcome of initial antiretroviral regimens in previously naive HIV-infected subjects. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:2125–2132. - PubMed
-
- Law WP, Duncombe CJ, Mahanontharit A, Boyd MA, Ruxrungtham K, Lange JM, et al. Impact of viral hepatitis co-infection on response to antiretroviral therapy and HIV disease progression in the HIV-NAT cohort. AIDS. 2004;18:1169–1177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI035042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5-M01-RR-00722/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK074348/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-37613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000722/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-37984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035040/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00425/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DK074348/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037984/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35043/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI037613/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI-35041/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

