Image fusion using CT, MRI and PET for treatment planning, navigation and follow up in percutaneous RFA
- PMID: 19550401
- PMCID: PMC2850071
Image fusion using CT, MRI and PET for treatment planning, navigation and follow up in percutaneous RFA
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the feasibility of fusion of morphologic and functional imaging modalities to facilitate treatment planning, probe placement, probe re-positioning, and early detection of residual disease following radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of cancer.
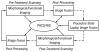
Methods: Multi-modality datasets were separately acquired that included functional (FDG-PET and DCE-MRI) and standard morphologic studies (CT and MRI). Different combinations of imaging modalities were registered and fused prior to, during, and following percutaneous image-guided tumor ablation with radiofrequency. Different algorithms and visualization tools were evaluated for both intra-modality and inter-modality image registration using the software MIPAV (Medical Image Processing, Analysis and Visualization). Semi-automated and automated registration algorithms were used on a standard PC workstation: 1) landmark-based least-squares rigid registration, 2) landmark-based thin-plate spline elastic registration, and 3) automatic voxel-similarity, affine registration.
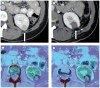
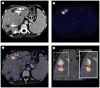
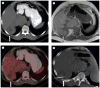
Results: Intra- and inter-modality image fusion were successfully performed prior to, during and after RFA procedures. Fusion of morphologic and functional images provided a useful view of the spatial relationship of lesion structure and functional significance. Fused axial images and segmented three-dimensional surface models were used for treatment planning and post-RFA evaluation, to assess potential for optimizing needle placement during procedures.
Conclusion: Fusion of morphologic and functional images is feasible before, during and after radiofrequency ablation of tumors in abdominal organs. For routine use, the semi-automated registration algorithms may be most practical. Image fusion may facilitate interventional procedures like RFA and should be further evaluated.
Figures


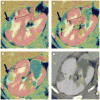

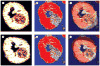
References
-
- Kramer EL, Noz ME, Sanger JJ, et al. CT-SPECT fusion to correlate radiolabeled monoclonal antibody uptake with abdominal CT findings. Radiology. 1989;172:861–5. - PubMed
-
- Pietrzyk U, Herholz K, Fink G, et al. An interactive technique for three-dimensional image registration: validation for PET, SPECT, MRI and CT brain studies. J Nucl Med. 1994;35:2011–8. - PubMed
-
- Wahl RL, Quint LE, Cieslak RD, et al. “Anatometabolic” tumor imaging: fusion of FDG PET with CT or MRI to localize foci of increased activity. J Nucl Med. 1993;34:1190–7. - PubMed
-
- Mountz JM, Zhang B, Liu HG, Inampudi C. A reference method for correlation of anatomic and functional brain images: validation and clinical application. Semin Nucl Med. 1994;24:256–71. - PubMed
-
- Correia JA. Registration of nuclear medicine images. J Nucl Med. 1990;31:1227–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
