Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the NKp30 receptor
- PMID: 19551844
- PMCID: PMC6357774
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23054
Myeloid derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma via the NKp30 receptor
Abstract
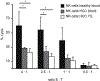
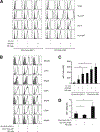
Several immune suppressive mechanisms that evade the host immune response have been described in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); one of these mechanisms is expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). MDSCs have been shown to inhibit T cell responses in tumor-bearing mice, but little is known about these cells in humans. Here, we have analyzed and characterized the effect of MDSCs on the innate immune system, in particular, their interaction with natural killer (NK) cells in patients with HCC. MDSCs from patients with HCC inhibited autologous NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion when cultured together in vitro. This suppression was dependent on cell contact, but did not rely on the arginase activity of MDSCs, which is a hallmark function of these cells. However, MDSC-mediated inhibition of NK cell function was dependent mainly on the NKp30 on NK cells.
Conclusion: Our study suggests a new role for MDSCs in patients with HCC in disarming the innate immune system and further contributing to the immune suppressor network in these patients. These findings have important implications when designing immunotherapy protocols.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report
Figures
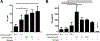
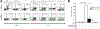


Similar articles
-
A new population of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma patients induces CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) T cells.Gastroenterology. 2008 Jul;135(1):234-43. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.020. Epub 2008 Mar 21. Gastroenterology. 2008. PMID: 18485901
-
Deficient Natural Killer Cell NKp30-Mediated Function and Altered NCR3 Splice Variants in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepatology. 2019 Mar;69(3):1165-1179. doi: 10.1002/hep.30235. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30153337
-
Targeting the crosstalk between cytokine-induced killer cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Hepatol. 2019 Mar;70(3):449-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.10.040. Epub 2018 Nov 9. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 30414862 Free PMC article.
-
Immune responses in hepatocellular carcinoma.Dig Dis. 2010;28(1):150-4. doi: 10.1159/000282079. Epub 2010 May 7. Dig Dis. 2010. PMID: 20460904 Review.
-
Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells Interactions With Natural Killer Cells and Pro-angiogenic Activities: Roles in Tumor Progression.Front Immunol. 2019 Apr 18;10:771. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00771. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31057536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intratumor Regulatory Noncytotoxic NK Cells in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2021 Mar 10;10(3):614. doi: 10.3390/cells10030614. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33802077 Free PMC article.
-
EP2 and EP4 blockade prevents tumor-induced suppressive features in human monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 26;15:1355769. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1355769. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38343540 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSC), macrophages, and dendritic cells enhances tumor-induced immune suppression.Semin Cancer Biol. 2012 Aug;22(4):275-81. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.01.011. Epub 2012 Feb 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012. PMID: 22313874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:159269. doi: 10.1155/2015/159269. Epub 2015 May 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 26078490 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells regulate natural killer cell response to adenovirus-mediated gene transfer.J Virol. 2012 Dec;86(24):13689-96. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01595-12. Epub 2012 Oct 10. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 23055553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Serafini P, Borrello I, Bronte V. Myeloid suppressor cells in cancer: recruitment, phenotype, properties, and mechanisms of immune suppression. Semin Cancer Biol 2006;16:53–65. - PubMed
-
- Pak AS, Wright MA, Matthews JP, Collins SL, Petruzzelli GJ, Young MR. Mechanisms of immune suppression in patients with head and neck cancer: presence of CD34(+) cells which suppress immune functions within cancers that secrete granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin Cancer Res 1995;1:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Zea AH, Rodriguez PC, Atkins MB, Hernandez C, Signoretti S, Zabaleta J,et al.Arginase-producingmyeloidsuppressorcellsinrenalcellcarcinoma patients: a mechanism of tumor evasion. Cancer Res 2005;65:3044–3048. - PubMed
-
- Almand B, Clark JI, Nikitina E, van Beynen J, English NR, Knight SC, et al. Increased production of immature myeloid cells in cancer patients: a mechanism of immunosuppression in cancer. J Immunol 2001;166:678–689. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
